Muscle anatomy, a marvel of biological engineering, encompasses a complex array of structures each with distinct functions vital to the body’s movement and health. Among these, the sarcolemma and endomysium play pivotal roles, yet their differences often remain unclear to many. These components, though both essential in muscle function, serve unique purposes and exhibit distinct structural properties.
The sarcolemma is the thin, plasma membrane encasing muscle cells, crucial for initiating muscle contraction and maintaining the balance of ions across the muscle fiber. On the other hand, the endomysium is a delicate layer of connective tissue that wraps each muscle fiber, providing support and flexibility while facilitating nutrient delivery to the muscles. Understanding the distinction between these two structures is key to comprehending how muscles operate and maintain their health.
Focusing on these differences enriches our understanding of muscle physiology and highlights the intricate design of our musculoskeletal system. By exploring the unique characteristics and functions of the sarcolemma and endomysium, we gain insights into their critical roles in muscle contraction, repair, and overall health, thereby shedding light on the complexity and elegance of human anatomy.
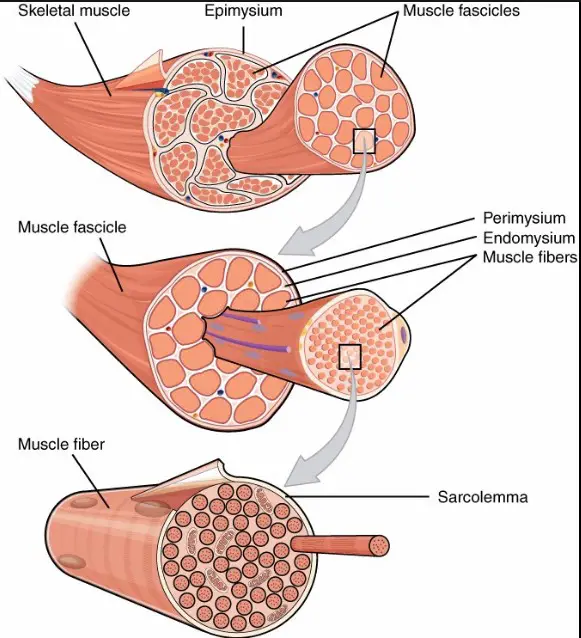
Muscle Structure Overview
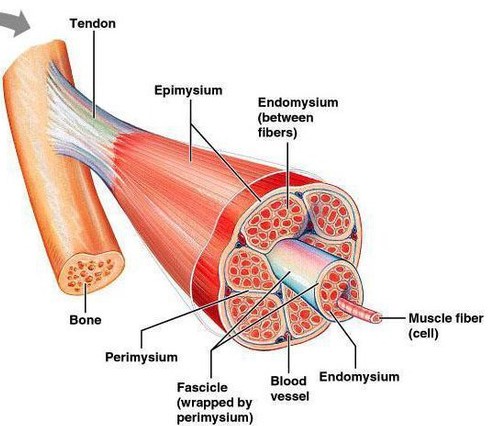
Basic Muscle Anatomy
Muscles are the engines of our body, converting energy into force. They enable us to move, speak, breathe, and perform the simplest to the most complex tasks of daily living. At its core, muscle tissue is categorized into three main types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Each type has a unique structure and a specific role within the body. Skeletal muscles attach to bones and control voluntary movements. Cardiac muscle makes up the heart, pumping blood throughout the body. Smooth muscle is found in walls of organs and blood vessels, managing the flow of substances through the body.
Microscopic Muscle Components
Role of Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Each fiber is a single cell that contracts in response to neural stimulation. This contraction is the fundamental action that drives movement. Muscle fibers are bundled together, surrounded by connective tissue, to form a muscle.
Introduction to Muscle Cell Structures
Within each muscle fiber are smaller structures essential to its function. Myofibrils, long strands of proteins actin and myosin, are crucial for muscle contraction. Surrounding each muscle fiber is the sarcolemma, a membrane that plays a key role in transmitting the electrical signals necessary for muscle contraction. Within the connective tissue, the endomysium supports each individual muscle fiber, providing structural integrity and flexibility.
What is Sarcolemma?
Definition and Function
The sarcolemma is the plasma membrane that surrounds muscle cells. It is more than just a barrier; it plays an active role in muscle function and health. The sarcolemma works to transmit electrical signals, maintain the balance of ions across the membrane, and integrate signals that lead to muscle contraction.
Sarcolemma as the Muscle Cell Membrane
This thin, pliable layer encases the muscle fiber’s contents, protecting them while also being permeable enough to allow for necessary exchanges with the surrounding environment.
Its Role in Muscle Function and Health
The sarcolemma’s ability to propagate electrical impulses is vital for initiating muscle contractions. These impulses trigger the release of calcium ions within the muscle cells, leading to the sliding of actin and myosin filaments past each other, and ultimately, muscle contraction.
Structure of Sarcolemma
Physical Characteristics
The sarcolemma consists of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that facilitate its functions. It is flexible yet sturdy, capable of withstanding the changes in muscle fiber size that occur during contraction and relaxation.
Composition and Related Structures
Beneath the sarcolemma is the sarcoplasm, the cytoplasm of muscle cells, which contains the organelles and molecules necessary for the cell’s function. The transverse tubules (T-tubules) are invaginations of the sarcolemma that penetrate into the cell’s interior, ensuring that the electrical signal reaches all parts of the muscle fiber simultaneously.
What is Endomysium?
Definition and Purpose
The endomysium is a type of connective tissue that wraps around each individual muscle fiber. It provides essential support and separation from neighboring fibers, allowing for efficient muscle contraction and flexibility.
Endomysium as Connective Tissue
Composed of reticular fibers and a base substance, the endomysium binds to the sarcolemma of each muscle fiber, ensuring that each cell maintains its structural integrity and position within the muscle.
Its Function in Muscle Integrity and Flexibility
The endomysium plays a crucial role in the health and functionality of muscle tissue. It allows muscles to glide smoothly against each other, reduces friction, and distributes force generated during muscle contraction.
Structure of Endomysium
Physical Properties
This delicate layer is thin yet durable, capable of stretching as the muscle fiber contracts and elongates.
Composition and Surrounding Tissues
The endomysium contains a rich supply of capillaries and nerve fibers that provide the muscle fibers with nutrients and neural connections, critical for their survival and function.
Key Differences
Structural Differences
The sarcolemma and endomysium differ significantly in their structure and location. The sarcolemma is a membrane directly surrounding the muscle cell, while the endomysium is a connective tissue layer that encases each muscle fiber within a muscle.
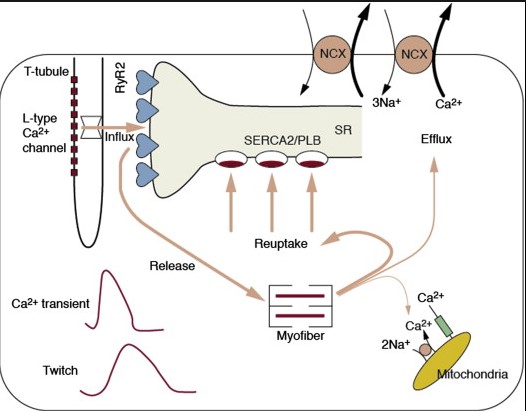
Importance in Muscle Health
Muscle health is fundamental to the smooth operation of the human body, allowing for movement, stability, and vital physiological processes. Two microscopic structures play crucial roles in maintaining muscle health: the sarcolemma and the endomysium. Their contributions, though often overlooked, are essential for muscle function, repair, and overall health.
Sarcolemma’s Role
In Muscle Contraction and Nutrient Exchange
The sarcolemma acts as the muscle cell’s protective barrier, orchestrating a plethora of critical functions that ensure muscle health. Its primary role is in muscle contraction, where it transmits signals that trigger these contractions, essential for movement and stability. Moreover, it facilitates nutrient exchange between the muscle cells and their surrounding environment. This exchange is vital for providing muscles with the oxygen and nutrients needed for energy production, recovery, and growth.
Endomysium’s Contribution
In Muscle Repair, Growth, and Protection
The endomysium surrounds individual muscle fibers, playing a key role in muscle repair and growth. It provides a supportive framework that helps maintain muscle integrity and flexibility. Following injury or stress, it aids in the repair process, ensuring that muscle fibers are correctly aligned and that new fibers are formed as needed. Additionally, the endomysium’s supportive network protects muscle fibers from external forces, minimizing the risk of damage.
Case Studies
Exploring real-world examples highlights the critical importance of both the sarcolemma and endomysium in muscle health and disease management.
Sarcolemma in Muscle Diseases
Conditions such as muscular dystrophy and myopathies often involve complications with the sarcolemma. For instance, mutations affecting proteins associated with the sarcolemma can lead to its weakening, making muscle fibers more susceptible to damage during contraction. This vulnerability can result in progressive muscle weakness and degeneration, underscoring the sarcolemma’s pivotal role in muscle health.
Endomysium and Muscle Disorders
Similarly, diseases like fibromyalgia and inflammatory myopathies can affect the endomysium. These conditions may lead to inflammation or alterations in the endomysium’s structure, affecting its ability to support and protect muscle fibers. Understanding the endomysium’s involvement in these disorders is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies.
Prevention and Care
Maintaining the health of the sarcolemma and endomysium is essential for preventing muscle-related diseases and ensuring optimal muscle function.
Protecting Sarcolemma Health
To maintain sarcolemma integrity, consider the following tips:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in a balanced mix of cardiovascular and strength-training activities to enhance muscle strength and sarcolemma health.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: Consume foods high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to support cellular health and prevent oxidative stress.
- Adequate Hydration: Ensure proper hydration to maintain cellular function and facilitate nutrient exchange.
Maintaining Healthy Endomysium
For endomysium health, implement these strategies:
- Stretching and Flexibility Exercises: Promote muscle flexibility and integrity by incorporating regular stretching into your routine.
- Proper Rest and Recovery: Allow muscles to recover adequately between intense workouts to prevent overuse injuries and support tissue repair.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Include anti-inflammatory foods in your diet to reduce the risk of inflammation that can affect the endomysium.
FAQs
What is the Sarcolemma?
The sarcolemma is the outer membrane of a muscle fiber, functioning as a barrier and playing a critical role in the transmission of electrical signals necessary for muscle contraction. It’s vital for the coordination of muscular responses and acts as the interface between the muscle cell’s internal environments and the extracellular space.
How does Endomysium support muscle fibers?
Endomysium surrounds each individual muscle fiber, providing structural support and elasticity. This fine layer of connective tissue helps in the distribution of nutrients and oxygen to the muscle cells, facilitating the repair and growth processes. It’s essential for maintaining the integrity and proper functioning of muscle fibers.
Can damage to Sarcolemma affect muscle function?
Yes, damage to the sarcolemma can significantly impair muscle function. It disrupts the normal flow of ions, affecting the muscle cell’s ability to contract. This can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and in severe cases, muscular dystrophy or other neuromuscular disorders.
What role does the Endomysium play in muscle regeneration?
The endomysium plays a crucial role in muscle regeneration by providing a scaffold for new muscle fibers to grow. It contains various growth factors and cells responsible for tissue repair and regeneration. This connective tissue layer is vital for recovering from muscle injuries and maintaining muscle mass.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the sarcolemma and endomysium unveils the complexity and sophistication of muscle anatomy. These structures, though differing in function and location, are integral to the muscle’s ability to contract, repair, and perform efficiently. Their roles underscore the importance of cellular and extracellular components working in harmony for the body’s mobility and health.
This exploration not only deepens our appreciation for the intricate workings of the human body but also emphasizes the significance of maintaining muscle health. Recognizing how these microscopic structures contribute to our physical capabilities can inspire efforts towards better fitness, injury prevention, and overall well-being.