The body is a complex machine that needs to be in balance in order to work correctly. One way it is able to do this is through a system of hormones, which can be divided into two categories: endocrine and exocrine.
In this blog, we will explore the differences between these two types of hormones and how they work together to keep the body functioning properly.
How endocrine and exocrine glands function differently
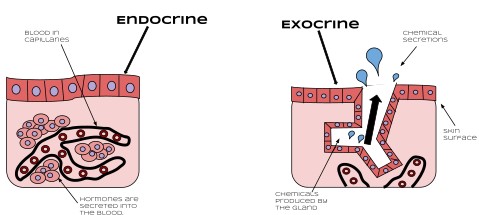
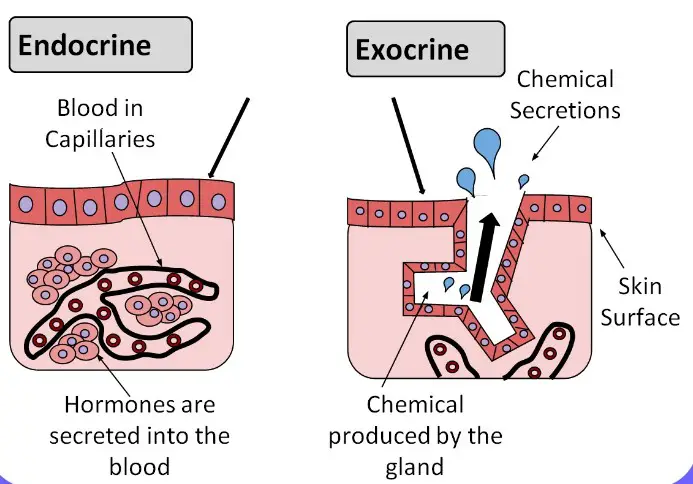
Endocrine and exocrine glands are both integral parts of the human body’s internal system, but they function in different ways. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts that lead to the outside of the body.
Endocrine glands are responsible for regulating body functions such as metabolism and growth, while exocrine glands help with digestion, reproduction, and kidney function. Endocrine glands are relatively small and release hormones in response to stimuli from the body, while exocrine glands are larger and release substances in response to signals from the nervous system.
The endocrine system is considered the “master gland” of the body, while the exocrine system helps to regulate the digestive system and other bodily processes. It’s important to understand the differences between these two systems in order to maintain optimal health and wellness.
Examples of endocrine and exocrine glands
The human body is made up of many different types of glands that produce and secrete various substances. Endocrine and exocrine glands are two distinct types that have distinct roles in the body. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts that eventually lead to the outside of the body.
Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands secrete substances into ducts that eventually lead to the outside of the body. Endocrine glands play an important role in controlling metabolism, growth and development, and sexual function. Examples of endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
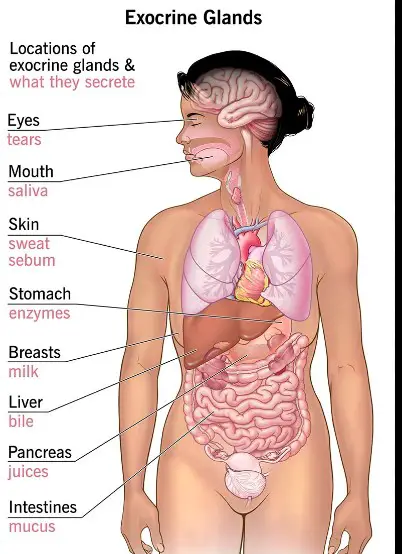
On the other hand, exocrine glands produce substances such as sweat, saliva, and mucus. Examples of exocrine glands include the sweat glands, salivary glands, and pancreas.
Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts that open to the outside of the body.
Hormones produced by endocrine and exocrine glands
The human body is a complex network of organs and glands that produce hormones to regulate various functions. Endocrine and exocrine glands are the two main types of glands responsible for producing hormones.
Endocrine hormones are produced by the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. These hormones help regulate metabolic processes, such as growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
Exocrine hormones, on the other hand, are produced by sweat glands, salivary glands, pancreas, and other glands. These hormones control the production of sweat and saliva, as well as the release of digestive enzymes.
By understanding the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands, we can better understand the role of hormones in our bodies.
Disorders associated with endocrine and exocrine glands
The endocrine and exocrine glands are both essential for our body’s functioning and health, but they serve different purposes. Endocrine glands produce hormones that enter the bloodstream and act as chemical messengers, while exocrine glands produce substances that are released directly into the ducts or cavities of the body. Endocrine disorders, such as diabetes, occur when the hormone-producing glands do not produce enough hormones or fail to respond to hormones.
Exocrine disorders, such as pancreatic insufficiency, occur when the ducts or cavities of the body are blocked or the glands produce too much or too little of the substance that they are responsible for producing. Both endocrine and exocrine disorders can have serious health consequences, so it is important to understand the difference between them and seek medical treatment as soon as possible.
Benefits of having both endocrine and exocrine glands
The body is an amazing and intricate system made up of many different components, including both endocrine and exocrine glands. But what is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands?
Both types of glands serve important functions in the body, so it can be beneficial to have both. Endocrine glands are responsible for the regulation of hormones, which play a role in everything from metabolism and growth, to reproduction and sleep.
An example of an endocrine gland is the thyroid, which releases hormones into the bloodstream that help regulate metabolism. Exocrine glands secrete substances into a duct or tube, which then carries the substance to its target organ or tissue. Examples of exocrine glands include the sweat glands, which secrete sweat to help cool the body, and the salivary glands, which secrete saliva to help break down food in the mouth.
By having both endocrine and exocrine glands, the body is able to effectively regulate hormones and secrete substances to different areas of the body. This helps to ensure that the body is functioning properly and able to carry out its necessary functions.
Final Touch
In conclusion, endocrine and exocrine glands are two types of glands that secrete hormones and other chemicals into the body. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands release their secretions through ducts into target organs or tissues.
Both types of glands are important for maintaining a healthy body.