Human bodies are as diverse as personalities, each shaped by unique genetic and environmental factors. This variety can be broadly categorized into three primary body types: ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph. Each type responds differently to diet and exercise, influencing individual health, fitness strategies, and physical appearance.
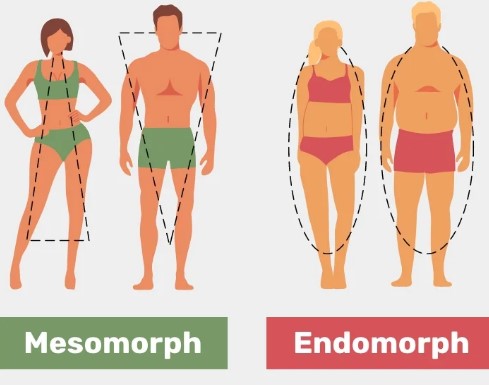
The primary distinction between ectomorphs, mesomorphs, and endomorphs lies in their physical build and metabolic rate. Ectomorphs are typically lean and struggle to gain weight, mesomorphs find it relatively easy to gain and lose weight and are naturally muscular, and endomorphs have a higher body fat percentage and a slower metabolism, which makes it challenging for them to lose weight.
Recognizing your body type is not about labeling or restricting potential but about understanding how to optimize your personal health and fitness strategy. Each body type has its strengths and limitations, which, when acknowledged, can lead to a more tailored and effective approach to nutrition, exercise, and general well-being.
Body Type Basics
Definition of Body Types
The concept of body types, or somatotypes, classifies individuals based on their physique and predispositions in metabolism and frame. Traditionally, these are segmented into three categories: ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph. Each type has distinct characteristics that affect nutritional needs, workout effectiveness, and overall health strategies.
Historical Background
The classification into ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph was pioneered by psychologist William Sheldon in the early 1940s. Sheldon believed that one’s body type could predict their personality and temperament. Although modern science has moved away from these psychological associations, the physical classifications remain useful in fields like sports science and nutrition.
Significance in Fitness and Health
Understanding one’s body type is crucial for developing personalized fitness and health plans. Each type responds differently to food and exercise, impacting weight management, muscle growth, and overall health. Tailoring nutrition and fitness routines to your body type can lead to more effective results and optimized health.
Ectomorph Characteristics
Physical Features
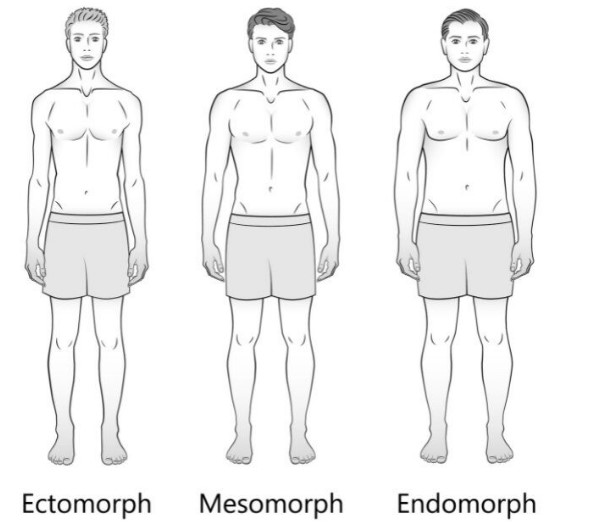
Ectomorphs are typically characterized by a slim, lean build with small joints and lean muscle. They usually have long limbs and little body fat with a flat chest. This body type often struggles to gain weight due to their fast metabolism.
Metabolic Traits
Ectomorphs have a high metabolic rate that burns calories quickly, which is why gaining weight and muscle can be a challenge. Their bodies are more efficient at carbohydrate processing and have a higher carbohydrate tolerance.
Common Health and Fitness Challenges
- Difficulty in gaining muscle mass
- Struggles with weight gain despite high-calorie diets
- Faster fatigue during high-resistance training
Mesomorph Characteristics
Physical Features
Mesomorphs are naturally muscular and well-built. They have a large bone structure, large muscles, and a naturally athletic physique with a high capacity for muscle growth. This body type is often considered the most advantageous for physical strength and aesthetics.
Metabolic Traits
Mesomorphs benefit from a balanced metabolism that is not too quick but efficient enough to prevent excessive fat gain. This allows for easier muscle gains and effective management of body weight.
Common Health and Fitness Challenges
- Tendency to gain fat more easily than ectomorphs
- Potential overconfidence in diet flexibility, which can lead to unbalanced eating habits
- Difficulty in fine-tuning body aesthetics beyond basic fitness
Endomorph Characteristics
Physical Features
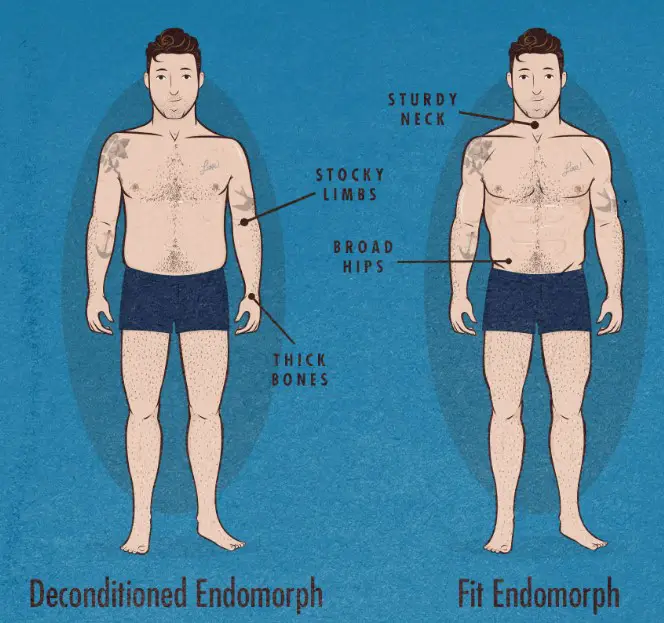
Endomorphs generally have a higher fat accumulation, wider waist, and a larger bone structure. This body type is predisposed to storing fat rather than building muscle. Endomorphs often find it difficult to lose weight and maintain a lean physique.
Metabolic Traits
The metabolic rate in endomorphs is slower, which contributes to weight gain and difficulty in losing fat. They have a lower carbohydrate tolerance, which necessitates careful monitoring of diet, particularly refined sugars and flours.
Common Health and Fitness Challenges
- High susceptibility to weight gain
- Struggles with maintaining weight loss
- Requires more strict dietary constraints to manage weight
Comparing Body Types
Physical Comparison
While ectomorphs are lean, mesomorphs are muscular, and endomorphs are more rounded. These physical characteristics significantly influence each type’s athletic abilities and aesthetic.
Metabolic Rate Comparison
Ectomorphs have a fast metabolism, making it hard to gain weight. Mesomorphs have a balanced metabolism, aiding in easier muscle gain and weight management. Endomorphs struggle with a slow metabolism, often leading to weight gain.
Exercise Preferences
- Ectomorphs: Benefit from lower cardio, high-calorie diets, and strength training.
- Mesomorphs: Excel in power and strength exercises; benefit from mixed cardio and resistance training.
- Endomorphs: Need high-intensity training and low-carb diets to manage weight effectively.
Diet Recommendations
Ectomorph Diet Focus
Ectomorphs need a high-calorie intake to counteract their speedy metabolism. The ideal diet should focus on:
- High carbohydrates: Aim for 50-60% of daily calories from carbs to fuel energy needs.
- Protein-rich foods: Incorporate protein in every meal to aid muscle repair and growth. Target 1.5-2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
- Frequent meals: Eating every 2-3 hours can help in maintaining calorie intake and managing fast metabolism.
Mesomorph Diet Focus
Mesomorphs, with their efficient metabolism, can benefit from a balanced diet:
- Moderate carbohydrates: About 40% of daily calories from carbs.
- Proteins: Important for muscle maintenance. Aim for 1.2-1.5 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Healthy fats: Essential for hormone production and overall health. About 20-30% of daily calories.
Endomorph Diet Focus
Endomorphs need to manage calorie intake carefully to avoid unwanted weight gain:
- Low carbohydrates: Reduce carb intake to 30-40% of daily calories, focusing on complex carbs.
- High protein: A higher protein intake helps with satiety and metabolism. Target around 1.5-2 grams per kilogram.
- Frequent, small meals: Helps manage hunger and improve metabolic rate.
Exercise Strategies
Best Practices for Ectomorphs
To gain muscle and weight, ectomorphs should focus on:
- Strength training: Less cardio, more weight-lifting with high intensity.
- Compound movements: Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses build major muscle groups.
- Adequate rest: Recovery is crucial as ectomorphs can easily overtrain.
Best Practices for Mesomorphs
Mesomorphs excel in various types of physical activities and should focus on:
- Variety in training: Combination of strength and cardio to maintain fitness without gaining excess fat.
- Regular challenge: Increasing the intensity or weight to continuously challenge the muscles.
- Recovery: Sufficient rest and recovery, alongside active recovery days.
Best Practices for Endomorphs
Endomorphs should aim to boost metabolism and lose fat through:
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): Effective for quick fat burning.
- Strength training: Focus on low to moderate weight and higher repetitions.
- Consistency: Regularity in workouts is key to sustaining weight loss.
Impact on Health
How Body Type Affects Overall Health
Each body type has predispositions that can influence long-term health outcomes:
- Ectomorphs might struggle with gaining weight, potentially leading to deficiencies if their diet lacks essential nutrients.
- Mesomorphs often maintain a balance but can easily tip into overweight if not careful.
- Endomorphs are at a higher risk for obesity-related diseases if they maintain a sedentary lifestyle.
Risk Factors Associated with Each Type
Understanding these risks can help in planning preventive measures:
- Ectomorphs: Bone density issues and lower body strength.
- Mesomorphs: Risk of cardiovascular disease with improper diet.
- Endomorphs: Increased likelihood of diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Lifestyle Modifications
Tips for Ectomorphs
- Caloric surplus: Focus on eating more than your caloric burn.
- Energy-dense snacks: Nuts, seeds, and avocados can help in quick, healthy weight gain.
Tips for Mesomorphs
- Balanced lifestyle: Equal focus on diet, exercise, and recovery.
- Monitor body composition: Regular checks to adjust diet and exercise as needed.
Tips for Endomorphs
- Activity boost: Keeping physically active throughout the day.
- Structured meals: Plan meals to avoid impulsive eating.
Psychological Aspects
Mental Health and Body Types
The link between body type and mental health is profound:
- Ectomorphs may feel pressure to gain weight or muscle, which can affect their self-esteem.
- Mesomorphs might face stereotypes about being athletic, influencing their self-image.
- Endomorphs often deal with societal pressure over body image, which can lead to stress and anxiety.
Self-perception and Body Image
Positive self-perception is crucial, regardless of body type:
- Self-acceptance: Embracing your natural physique.
- Healthy goals: Setting realistic and health-focused goals.
- Supportive environment: Surrounding oneself with positive influences and support systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines an ectomorph?
Ectomorphs are characterized by a slim, linear appearance with little body fat and muscle. They often have difficulty gaining weight due to a fast metabolic rate. Tailoring a diet rich in calories and engaging in strength training can help ectomorphs build mass.
How do mesomorphs differ from other types?
Mesomorphs naturally have a well-built, athletic body. They gain muscle easily and have an efficient metabolism that balances muscle gain and fat storage. Mesomorphs benefit from a balanced diet and varied physical routines that include strength and cardio training.
Why do endomorphs struggle with weight loss?
Endomorphs have a higher proportion of body fat and a tendency to store fat easily due to their slower metabolism. They can manage and reduce body weight effectively by adopting a low-carbohydrate diet and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to boost metabolism.
Can you change your body type?
While one’s basic skeletal and muscular structure is genetically determined, lifestyle changes like diet and exercise can modify how these traits are expressed. Through targeted strategies, individuals can enhance their natural body type for better health and fitness.
Conclusion
Understanding the different body types helps tailor lifestyle choices that align more closely with personal health and fitness goals. Whether you are an ectomorph struggling to gain muscle, a mesomorph looking to optimize strength, or an endomorph working towards weight loss, specific strategies can enhance your natural physique.
Embracing your body type is crucial for developing a sustainable approach to health and fitness. With the right knowledge and tools, anyone can create a balanced lifestyle that promotes physical well-being and personal satisfaction.