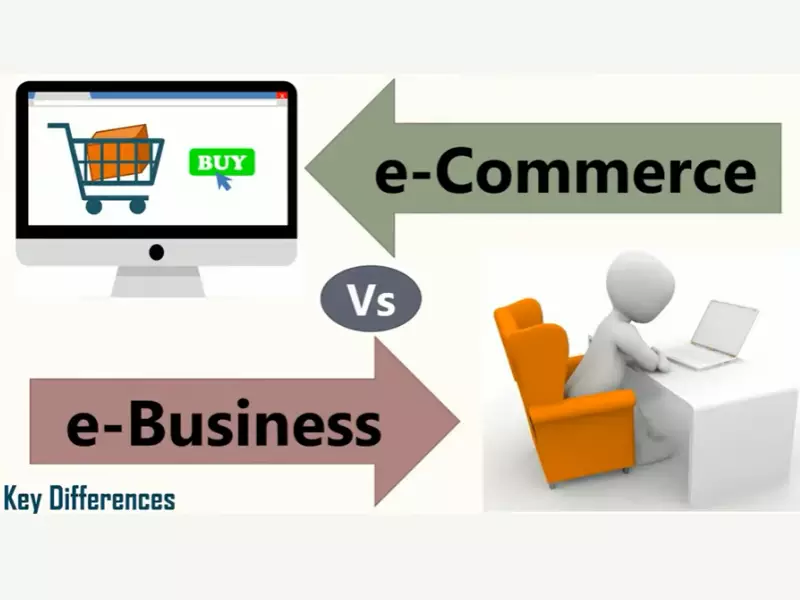
The digital landscape has fundamentally transformed how businesses operate and interact with their customers. At the heart of this transformation are two concepts often mentioned in tandem yet distinct in their nature: Ecommerce and Ebusiness. While both leverage the internet to streamline operations and enhance customer service, they serve different roles within the modern digital economy.
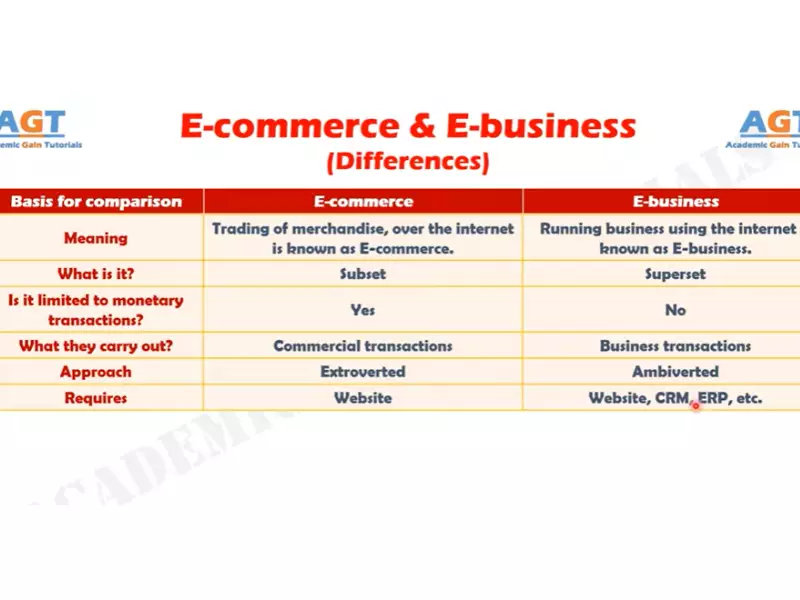
Ecommerce refers specifically to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It involves transactions that are facilitated online, from product selection to payment. On the other hand, Ebusiness encompasses a broader scope, including not just online transactions but also any business processes conducted over the internet, such as supply chain management, electronic data interchange, and customer relationship management.
The distinction between Ecommerce and Ebusiness is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage digital technologies for growth. Ecommerce focuses on the commercial transactions aspect, facilitating the direct exchange of goods and services. In contrast, Ebusiness covers a wider range of online business activities, integrating processes and systems to enhance overall business efficiency and relationships with stakeholders.
Core Concepts
Ecommerce Essentials
Definition and Scope
Ecommerce, short for electronic commerce, is the buying and selling of goods and services using the internet. It covers a range of online business activities for products and services. Ecommerce operates in four major market segments: business to business (B2B), business to consumer (B2C), consumer to consumer (C2C), and consumer to business (C2B).
Key Components
The backbone of ecommerce comprises several key components:
- Online Storefronts: The virtual presence where products or services are displayed.
- Shopping Carts: Enables consumers to accumulate a list of items for purchase.
- Payment Gateways: Secure payment systems that authorize payments.
- Security Measures: Protocols like SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to ensure data integrity and privacy.
- Logistics and Delivery Systems: The end-to-end delivery mechanism from seller to buyer.
Ebusiness Explained
Definition and Scope
Ebusiness (electronic business) is an even broader concept than ecommerce. It includes the buying and selling of goods and services, but extends to all aspects of running a business on the internet. This encompasses not just online transactions, but also activities such as supply chain management, electronic data interchange (EDI), online marketing, online transaction processing, and electronic funds transfer.
Core Elements
Ebusiness is built on several core elements:
- Digital Platforms: Websites and applications that host ebusiness operations.
- CRM Systems: Customer Relationship Management systems to manage customer interactions.
- ERP Systems: Enterprise Resource Planning systems integrate all facets of an operation.
- Data Analytics: Tools and techniques to analyze business data for insights.
Distinctions
Operational Focus
Ecommerce: Transactions
Ecommerce is focused on facilitating transactions. It’s about making sales and processing payments online. The operational focus is on customer conversion and the sales funnel — attracting visitors, converting them into customers, and conducting transactions securely.
Ebusiness: Broader Operations
Ebusiness, by contrast, involves a broader set of online business operations. Beyond transactions, it includes business processes like supply chain management, inventory management, customer service, and more. Ebusiness aims to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction across the board.
Technology Use
Platforms in Ecommerce
Ecommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce are tailored to support online stores. They offer tools for creating an online catalog, managing inventory, processing orders, and handling payments. These platforms are designed to facilitate easy setup and efficient management of online sales.
Systems in Ebusiness
Ebusiness relies on a wider array of systems, including ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software. These systems are essential for integrating various business processes, from order fulfillment to customer service, and providing a holistic view of the business operations.
Customer Interaction
Ecommerce Customer Engagement
In ecommerce, customer engagement is primarily transactional. The focus is on creating a smooth shopping experience, with user-friendly interfaces, personalized recommendations, and efficient checkout processes. The goal is to build trust and encourage repeat business by providing a seamless buying experience.
Ebusiness Client Relations
Ebusiness takes client relations further by leveraging data and technology to understand customer needs and build long-term relationships. Through CRM systems, businesses can track customer interactions, tailor marketing efforts, and offer personalized services. It’s about creating value for customers beyond the purchase.
Revenue Models
Ecommerce Revenue Sources
Ecommerce revenue primarily comes from direct sales. Businesses might also generate income through subscriptions, affiliate marketing, and advertising. The focus is on maximizing sales volume and transaction value.
Ebusiness Revenue Strategies
Ebusiness encompasses a broader range of revenue strategies. Beyond direct sales, it can include SaaS models (Software as a Service), licensing fees, and B2B services. Ebusiness strategies aim to leverage digital capabilities to create multiple revenue streams and enhance profitability.
Integration in Modern Business
The digital age has ushered in a new era of business operations, where the lines between ecommerce and ebusiness are increasingly blurred. Today, integration of these two domains is not just a strategy but a necessity for companies seeking to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Blending Ecommerce and Ebusiness
Blending ecommerce and ebusiness involves leveraging the strengths of both to create a cohesive, efficient, and customer-focused business model. This integration can take many forms, from incorporating digital marketing strategies to streamline the online shopping experience to utilizing data analytics for enhanced decision-making processes.
Case Studies of Integration
Several leading companies have successfully integrated ecommerce and ebusiness practices to achieve remarkable growth and customer satisfaction. For instance, Amazon has used its vast ecommerce platform to build an ebusiness empire, encompassing cloud computing services, AI technology, and a vast logistics network. Similarly, Zara has harnessed the power of real-time data from its online sales and social media to make fast, effective decisions about production and inventory management, blurring the lines between online sales and broader business operations.
Challenges and Solutions
Overcoming Integration Hurdles
The path to successful integration is fraught with challenges, from technological barriers to organizational resistance. Solutions involve:
- Adopting Scalable Technology: Implementing flexible, scalable solutions that can grow with the business.
- Cultural Change Management: Cultivating a digital-first culture that embraces change and innovation.
- Data Integration: Ensuring seamless flow and accessibility of data across all business functions.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Keeping the customer experience at the core of integration efforts.
Future Trends
As we look to the future, it’s clear that technology and market dynamics will continue to evolve, shaping the landscape of ecommerce and ebusiness.
Evolving Technologies
Impact on Ecommerce
Emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and blockchain are set to transform the ecommerce experience. AR and VR can offer more immersive shopping experiences, allowing customers to try before they buy in a virtual environment. Blockchain technology promises enhanced security and transparency for online transactions, building trust in the ecommerce ecosystem.
Influence on Ebusiness
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing ebusiness processes, from predictive analytics in inventory management to personalized customer service via chatbots. These technologies enable businesses to automate routine tasks, predict customer behavior, and deliver more personalized experiences.
Market Dynamics
Changing Consumer Behavior
Today’s consumers expect more than just a product or service; they seek a seamless, personalized shopping experience. They are more informed, more connected, and more discerning. Businesses must adapt by integrating ecommerce and ebusiness practices to meet these evolving expectations, offering convenience, speed, and customization.
Emerging Business Models
The rise of the sharing economy, subscription services, and platform-based business models reflects a shift towards more flexible, service-oriented business practices. Companies like Uber, Airbnb, and Netflix have demonstrated the power of leveraging digital platforms to disrupt traditional industries. This trend towards service and platform models shows no signs of slowing down, highlighting the need for businesses to continuously innovate and integrate digital practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between Ecommerce and Ebusiness?
The main difference lies in their scope and focus. Ecommerce is specifically about executing transactions online—selling and buying products or services on the internet. Ebusiness, however, extends beyond just transactions to encompass all aspects of running a business online, including managing internal processes, electronic data interchange, and customer relationship management.
How does Ecommerce enhance customer experiences?
Ecommerce enhances customer experiences by providing convenience, wider selection, competitive pricing, and personalized service. It allows customers to shop from anywhere at any time, compare products and prices easily, and receive tailored recommendations based on their shopping history and preferences.
Can a business be both Ecommerce and Ebusiness?
Yes, a business can operate as both Ecommerce and Ebusiness. Many companies start with Ecommerce activities, such as online sales, and gradually integrate broader Ebusiness practices like automating business processes, utilizing data analytics for decision-making, and engaging in digital marketing strategies to manage relationships with customers and suppliers more effectively.
What are the technological requirements for Ebusiness?
Ebusiness requires a robust technological infrastructure, including a well-designed website, eCommerce platforms, secure payment processing systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, supply chain management systems, and data analytics tools. These technologies enable efficient online operations, data exchange, and customer interactions.
Conclusion
In sum, while Ecommerce and Ebusiness may seem interchangeable, they represent different facets of the digital business world. Ecommerce focuses on the transactional aspect of online buying and selling, offering a direct path to consumer engagement and sales. Ebusiness, with its broader purview, integrates all online business activities, fostering operational efficiency, strategic management, and enhanced customer relationships.
Recognizing the distinction between these two is more than academic; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to thrive in the digital era. By understanding and leveraging the strengths of both Ecommerce and Ebusiness, companies can more effectively navigate the complexities of the digital marketplace, adapt to its evolving demands, and carve out a successful path in the online business landscape.
