Muscle contractions are fundamental to every motion the human body makes, from the simplest tasks like picking up a cup of coffee to complex movements seen in athletic performances. These contractions are not just mechanical reactions but involve a sophisticated process influenced by the type of contraction. Two primary types are concentric and eccentric contractions, each playing a pivotal role in daily activities and exercise regimens.
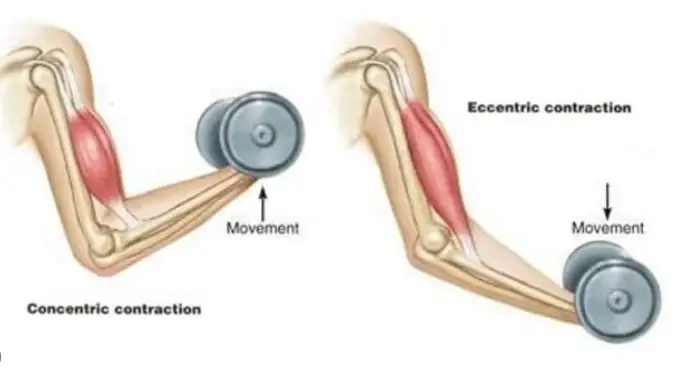
Concentric and eccentric contractions represent the muscle’s response to different movement demands. Concentric contractions occur when a muscle shortens under load, effectively pulling on bones to produce movement. In contrast, eccentric contractions happen as the muscle elongates while still under tension, often controlling or slowing down motion.
This distinction is crucial not only for understanding basic biomechanics but also for applying this knowledge to enhance physical training, rehabilitation, and overall muscular health. The ability of muscles to contract concentrically and eccentrically is central to athletic performance and injury prevention, reflecting their significance in health and fitness.
Muscle Contraction Basics
Definition and Types
Muscle contractions are fundamental physiological processes where muscle fibers shorten or lengthen to produce movement. They can be broadly categorized into three types: isometric, concentric, and eccentric. An isometric contraction occurs when the muscle exerts force without changing length, effectively holding a position against resistance. Concentric contractions involve the muscle shortening as it generates force, typically seen when lifting an object. Eccentric contractions are the opposite, occurring as the muscle elongates while still producing force, such as when lowering an object.
Role in Movement
Muscle contractions are crucial for all physical movements. From the basic act of walking to the complex mechanics of an athlete in action, muscle fibers contract in coordinated and specific patterns. These contractions not only facilitate movement but also maintain posture and stability. The human body relies on these muscular activities to manipulate the environment, express emotions through facial expressions, and perform involuntary functions like breathing and maintaining heartbeat.
Concentric Contractions
Characteristics
Concentric contractions are marked by the muscle shortening as it develops tension and overcomes opposing resistance. This type of contraction is most visible during the “positive” phase of an exercise. For example, when performing a bicep curl, the upward motion involves the biceps shortening as they pull the forearm upwards.
Examples in Daily Activities
Concentric contractions are a part of everyday activities that involve lifting or moving objects. When you stand up from a sitting position, your leg muscles perform concentric contractions. Other common examples include walking upstairs, jumping, and even the simple act of pushing a grocery cart.
Benefits in Exercise
Focusing on concentric contractions during exercise can lead to significant strength gains, increased muscle tone, and improved metabolic rate. Exercises that emphasize this type of contraction, such as weight lifting and resistance training, are particularly effective in building muscle mass and enhancing athletic performance. Concentric training is also associated with a lower risk of injury compared to other forms of exercise, as the muscle shortening process is naturally protective against muscle tears and strains.
Eccentric Contractions
Characteristics
Eccentric contractions occur as the muscle lengthens under tension. This happens typically during the “negative” phase of an exercise, such as when lowering a weight. Despite being less intuitive than concentric contractions, eccentric contractions are equally crucial. They often require the muscle to absorb energy, which can be more demanding and subsequently lead to greater strength and endurance improvements.
Common Examples
Everyday examples of eccentric contractions include walking down stairs or downhill, which involve the leg muscles lengthening to control the descent. Similarly, the act of sitting down gently uses eccentric contractions to slow the motion.
Benefits for Rehabilitation
Eccentric contractions are particularly beneficial in rehabilitation settings. They help improve the strength and function of muscles and tendons without imposing excessive stress. For patients recovering from muscle injuries or surgery, eccentric exercises can facilitate a quicker return to normal activity. They are also used to treat conditions like tendinopathy, as they can increase tendon strength and decrease sensitivity to pain.
Comparing Contractions
Key Differences
The fundamental distinction between concentric and eccentric contractions lies in the muscle’s behavior during exercise. In concentric contractions, muscles shorten as they exert force, typically seen during the upward motion of lifting weights. Eccentric contractions, on the other hand, involve muscles lengthening under tension, common during the lowering phase of the same activity. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing workout effectiveness and minimizing injury risks.
Visual Comparison Chart
To better illustrate the differences, consider a visual chart:
- Concentric Contractions: Muscle shortens, force exerted as it contracts (e.g., upward phase of a squat).
- Eccentric Contractions: Muscle lengthens, still exerting force but in an elongated state (e.g., downward phase of a squat).
This side-by-side comparison helps in visualizing how each contraction type functions during common exercises.
Impact on Muscle Growth
Eccentric contractions are often cited for their superior impact on muscle growth and strength development. They cause more microtears in the muscle fibers, which, when repaired, lead to stronger and larger muscles. This process, known as muscle hypertrophy, is enhanced by the increased tension generated during eccentric phases of an exercise. Concentric contractions also contribute to muscle building but are generally more effective for increasing muscular endurance and power.
Practical Applications
Sports and Training
Both types of muscle contractions are crucial in sports and training regimes. Athletes often focus on:
- Concentric-focused training for power sports like weightlifting and sprinting, where quick, explosive actions are crucial.
- Eccentric-focused training for sports requiring control and stability, such as downhill skiing or rock climbing.
Incorporating both contraction types in training can lead to balanced muscle development and improved overall athletic performance.
Physical Therapy Uses
In physical therapy, eccentric contractions are particularly valuable for rehabilitation from injuries. They are used to:
- Gradually increase the load on healing muscles and tendons without overstressing them.
- Improve the strength and flexibility of muscle groups with controlled, slow resistance training.
Concentric exercises are also used in later stages of therapy to build strength and ensure muscle function returns to pre-injury levels.
Injury Prevention Strategies
Understanding and applying the right balance of concentric and eccentric exercises can significantly reduce the risk of sports-related injuries. Training programs designed to enhance muscular balance and functional strength can prevent common issues like strains and sprains by:
- Strengthening the muscles and connective tissues.
- Increasing joint stability and mobility.
- Enhancing proprioception — the body’s ability to sense movement and position.
Recent Research Insights
Findings on Muscle Adaptations
Recent studies have shed light on how muscles adapt differently to concentric and eccentric training. Research indicates that eccentric training can lead to greater increases in muscle length (muscle hypertrophy) and improved metabolic efficiency. These adaptations are critical for athletes who require long-duration endurance and those recovering from muscle injuries.
Studies on Strength Training
Strength training research has consistently demonstrated that incorporating both types of contractions yields the best results. A study comparing the effects of concentric-only and eccentric-only training found that participants who engaged in both types of exercises showed improved muscle strength, greater endurance, and faster recovery times compared to those who focused on a single type.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are concentric contractions?
Concentric contractions occur when muscles shorten while generating force. This type of contraction is commonly observed when lifting weights during a bicep curl as the biceps contract to lift the weight upwards.
What are eccentric contractions?
Eccentric contractions happen when a muscle lengthens under tension, often during the lowering phase of an exercise. For example, when you lower a dumbbell in a bicep curl, the biceps are still contracting but in an elongating manner.
How do concentric and eccentric contractions differ?
The main difference between these contractions lies in their action on the muscle. Concentric contractions shorten the muscle to produce movement, while eccentric contractions control the motion by lengthening the muscle.
Why are eccentric contractions important?
Eccentric contractions are crucial for activities that require controlled movements, such as descending stairs. They help in energy absorption and reduce the force impact on joints, thus playing a significant role in injury prevention.
Can training eccentric contractions improve performance?
Yes, training that focuses on eccentric contractions can significantly improve muscular strength, endurance, and control. It enhances the muscle’s ability to handle higher loads and stresses, beneficial for both athletes and everyday activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, concentric and eccentric contractions are more than just biomechanical terms; they are integral to how we move, exercise, and even recover from injuries. Understanding the differences and applications of these contractions can dramatically influence one’s approach to fitness and rehabilitation.
By incorporating knowledge of both contraction types into training routines, individuals can optimize their physical capabilities and prevent injuries, ensuring a balanced and effective approach to muscle development and maintenance. This understanding not only enriches one’s fitness journey but also bolsters long-term muscular health and functionality.