Cilia, stereocilia, and microvilli are integral cellular structures that play crucial roles in the physiology of living organisms. Though they share some superficial similarities, their differences are significant and impact various bodily functions. These structures are not only essential for understanding basic biology but also for medical science as they influence various health conditions.
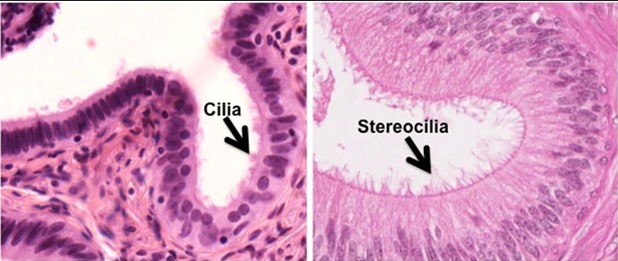
Cilia are primarily motile and found across almost all cell types, aiding in movement and sensory functions. Stereocilia, despite their name, are not true cilia but actin-based structures involved in sensory processes, notably in the inner ear. Microvilli, smaller and more uniform, increase surface area for absorption and secretion in epithelial cells.
These structures are vital for the correct functioning of many systems within the body. Their roles range from helping move fluids over epithelial surfaces to absorbing nutrients in the gut, highlighting their diversity in structure and function. This variety underpins not only basic cellular operations but also key human sensory and absorption mechanisms.
Cilia Overview
Definition and Structure
Cilia are small, hair-like structures that extend from the surface of many types of cells. They are composed of microtubules arranged in a specific pattern known as the “9+2” structure. This arrangement consists of nine pairs of microtubules forming a ring around two central microtubules. The entire structure is encased in the cell’s plasma membrane, allowing the cilium to move fluidly.
These structures can be classified into two types: motile cilia and primary cilia. Motile cilia are typically found on cells that line the respiratory tract where they play a critical role in moving mucus and trapped particles out of the lungs. Primary cilia, on the other hand, are often found on nearly every cell type and are important in cellular signaling pathways.
Role in Cell Function
Cilia perform various functions depending on their type and location within the body. In the respiratory system, motile cilia prevent the accumulation of mucus and debris by coordinating their movements to push substances towards the throat for expulsion. This is a critical defense mechanism against infections and buildup of foreign particles.
In the realm of sensory cells, cilia are essential for signal transduction. For example, in kidney cells, primary cilia act as sensors for fluid flow, which is crucial for normal kidney function and development. This sensory capability allows cells to adapt to their environment, influencing cellular responses and maintaining homeostasis.
Stereocilia Overview
Definition and Features
Stereocilia are not true cilia but are similar in appearance. These are elongated, microfilament-based structures that are larger than typical microvilli but share a common actin core. Unlike motile cilia, stereocilia do not move but are immobile and are tightly packed into bundles.
Found primarily in the sensory cells of the inner ear, particularly in the hair cells of the cochlea, stereocilia are crucial for the detection of sound. Their structure allows them to respond to fluid motion or mechanical forces that are translated into neural signals.
Function in Sensory Cells
In the auditory system, stereocilia bend in response to sound waves. This bending opens mechanically gated ion channels that trigger a change in the electrical potential of the hair cells. This change is then converted into a chemical signal that can be transmitted to the brain, allowing for the perception of sound.
Their role is not limited to hearing; in the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance, stereocilia help detect head movements and orientation changes. Their ability to convert mechanical stimuli into electrical signals is fundamental in maintaining balance and spatial orientation.
Microvilli Overview
Structural Description
Microvilli are tiny, finger-like projections that increase the surface area of the plasma membrane. Unlike cilia and stereocilia, microvilli contain actin filaments that are tethered by different proteins, which stabilize their structure. They are most abundantly found on epithelial cells lining the intestines, where they play a significant role in nutrient absorption.
Each microvillus is covered by a plasma membrane and has a core of actin filaments that are cross-linked by proteins such as fimbrin and villin. This configuration provides both stability and flexibility, allowing microvilli to maximize their role in absorption.
Functional Significance
The primary function of microvilli is to enhance the absorptive capacity of epithelial cells. By increasing the surface area, microvilli allow for a greater volume of enzymes and transporters to be present, which facilitates efficient absorption of nutrients. In the intestines, this is particularly important for the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates and proteins.
Microvilli also contain various enzymes that aid in the processing of molecules before they are absorbed. This enzymatic activity is crucial for the final stages of digestion, ensuring that nutrients are in the optimal form for absorption into the bloodstream.
Comparative Anatomy
Structural Differences
Cilia, stereocilia, and microvilli exhibit distinctive structural characteristics that suit their specific functions within the body. Cilia are generally larger and equipped with a complex motor apparatus, allowing them to move fluidly. This motility is facilitated by dynein arms that drive the bending movements necessary for their function. In contrast, stereocilia lack this motility and are rigid, supported by a dense core of actin filaments. They are not capable of active movement but can respond to mechanical stimuli such as sound vibrations. Microvilli, the smallest of the three, maximize surface area with a simple brush-like structure made up of tightly packed actin filaments, enhancing their role in absorption.
Location and Cellular Distribution
The distribution of these cellular structures varies significantly across different cell types and tissues:
- Cilia are found on nearly every type of cell but are prominently featured in the respiratory tract and the reproductive system.
- Stereocilia are localized primarily in the sensory hair cells of the inner ear.
- Microvilli are most abundant on the epithelial cells of the small intestine and kidney tubules.
This distribution underscores their specialized roles and the need for their presence in specific physiological contexts.
Functional Distinctions
Specific Roles in the Body
Each of these structures has evolved to perform tasks vital to the organism’s survival:
- Cilia move substances across cell surfaces, playing key roles in defense against pathogens and facilitating the movement of eggs down the fallopian tubes in females.
- Stereocilia are crucial in the auditory process, translating sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain interprets as sound.
- Microvilli increase the absorptive capacity of cells, crucial for efficient nutrient uptake in the intestines and reabsorption in the kidneys.
Impact on Health and Disease
Malfunction or structural abnormalities in any of these can lead to serious health conditions. For instance:
- Defects in cilia function can cause respiratory diseases and conditions like situs inversus, where the internal organs are mirrored from their normal positions.
- Damage to stereocilia can result in hearing loss or balance disorders.
- A decrease in microvilli function or number can lead to malabsorption syndromes, severely affecting nutritional status.
Cellular Signaling
Interaction with Cellular Pathways
Cilia and microvilli play integral roles in cellular signaling pathways that control a wide range of biological processes. Cilia, for example, are involved in the Hedgehog signaling pathway, crucial for developmental processes and tissue regeneration. Microvilli contain enzymes and transporters that send signals to the cell about nutrient levels and status, affecting metabolic responses.
Significance in Signaling
The role of these structures in signaling is critical for maintaining cellular and systemic homeostasis. They provide essential feedback mechanisms that help cells adapt to environmental changes and maintain physiological functions. For instance, primary cilia’s role in sensing mechanical signals in the kidney helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance.
Research and Advances
Recent Studies on Cilia, Stereocilia, and Microvilli
Recent research has unveiled significant insights into the structure and function of these cellular appendages. Studies on cilia have shown their critical roles in cell motility and fluid dynamics, influencing treatments for diseases like polycystic kidney disease and chronic respiratory diseases. Research on stereocilia has focused on understanding their role in age-related hearing loss, leading to advancements in cochlear implant technologies. Investigations into microvilli have detailed their role in nutrient absorption and the implications for treating malabsorption disorders.
Future Directions in Research
The future of research in this area is vibrant with potential for groundbreaking discoveries that could transform medical treatments and diagnostics. Genetic editing tools like CRISPR offer possibilities for correcting mutations that affect cilia and microvilli function, potentially addressing root causes of diseases. Additionally, advancements in imaging technologies promise even deeper insights into the minute structural changes within these structures that could lead to better understanding and new therapeutic targets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Cilia?
Cilia are microscopic, hair-like structures extending from the surface of many eukaryotic cells. They are involved in movement and sensory functions, helping cells respond to environmental stimuli.
How do Stereocilia function?
Stereocilia are non-motile and located primarily in the inner ear, where they play a critical role in the sensory reception of sound. They increase the cell’s surface area to facilitate the detection of mechanical vibrations.
What role do Microvilli play?
Microvilli are tiny, finger-like projections that enhance the surface area of epithelial cells, crucial for maximizing nutrient absorption, particularly in the intestines.
How do Cilia differ from Microvilli?
While cilia are motile and can move fluid or mucus across the cell surface, microvilli are strictly involved in absorption and secretion processes and are non-motile.
Are Stereocilia and Cilia the same?
No, stereocilia are structurally and functionally different from cilia. They are longer, immotile, and do not have the classic 9+2 structure of motile cilia, functioning mainly in sensory organs like the ear.
Conclusion
Cilia, stereocilia, and microvilli are fundamental to the proper functioning of various physiological processes, each playing distinct roles within the body. Their differences in structure and function reflect the complexity and specialization of cellular components in adapting to different biological roles.
Understanding these structures provides insights into their critical functions across different organ systems. This knowledge not only enriches our understanding of cell biology but also aids in diagnosing and treating diseases related to these essential cellular features.