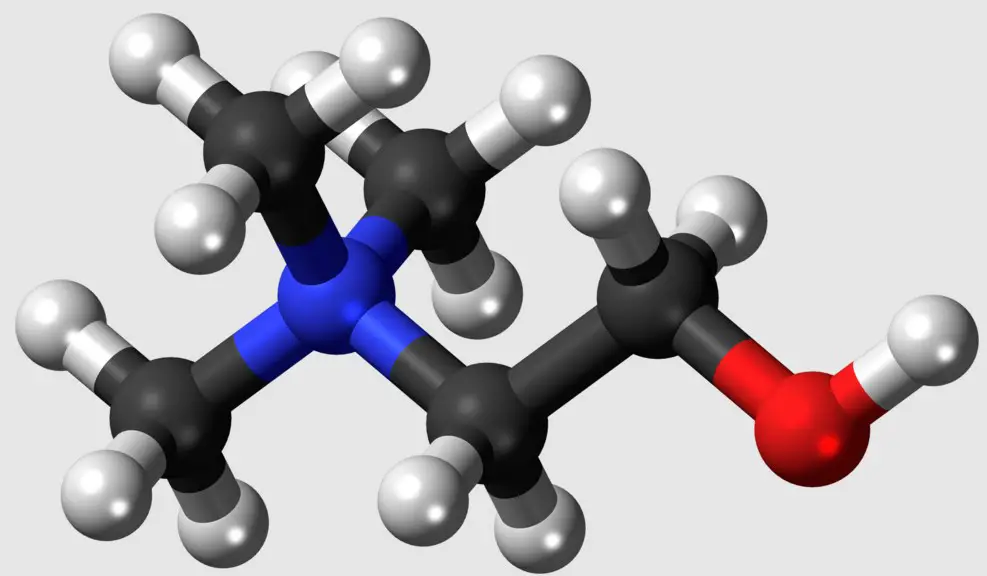
Choline and phosphatidylcholine are two crucial nutrients, often discussed in the realms of nutrition and health for their significant roles in the human body. Despite their importance, there’s a common cloud of confusion surrounding their differences, uses, and benefits. This ambiguity can lead to misconceptions about their dietary sources, functions, and the necessity of their supplementation.
Choline is an essential nutrient vital for liver function, normal brain development, nerve function, muscle movement, supporting energy levels, and maintaining a healthy metabolism. Phosphatidylcholine, on the other hand, is a compound that forms a crucial part of cell membranes and is made in the body from choline. It plays key roles in the process of methylation and is important for liver health, lipid metabolism, and neurological functions.
Understanding the distinction between choline and phosphatidylcholine is not just a matter of semantics. It involves recognizing their unique chemical structures, dietary sources, biological roles, and the synergistic way they contribute to health and disease prevention. With both nutrients playing pivotal roles in cognitive function, cardiovascular health, and beyond, their adequate intake is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
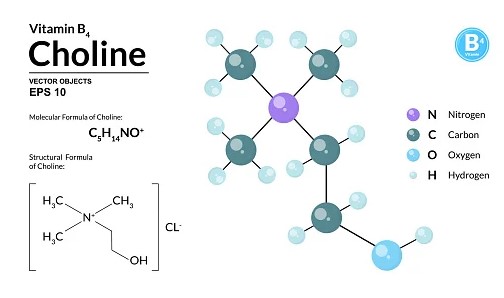
Choline Basics
Definition and Role in the Body
Choline is an essential nutrient that supports various bodily functions. It’s not typically considered a vitamin or mineral but plays a vital role similar to the B vitamins. Choline is crucial for:
- Brain development and function: It contributes to cognitive performance, memory, and mood.
- Liver health: Choline helps in the removal of fat from the liver, preventing diseases such as fatty liver disease.
- Muscle movement: It’s involved in the contraction of muscles.
- Metabolism: Choline plays a role in energy levels and maintaining a healthy metabolism.
- Cell structure: It’s essential for creating the phospholipids that make up cell membranes.
Sources of Choline
Choline is found in a variety of foods, making it accessible through a balanced diet. Major dietary sources include:
- Eggs: Particularly the yolks are rich in choline.
- Meat: Beef liver, chicken, and turkey are excellent sources.
- Fish: Salmon and cod offer significant amounts.
- Dairy products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese contain choline.
- Vegetables: Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and peas are good plant sources.
- Nuts and seeds: Particularly almonds and peanuts.
Daily Recommended Intake
The daily recommended intake of choline varies based on age, gender, and life stage:
- Adults (men): 550 mg/day
- Adults (women): 425 mg/day
- Pregnant women: 450 mg/day
- Breastfeeding women: 550 mg/day
Meeting these recommended intakes is crucial for optimal health and preventing deficiencies.
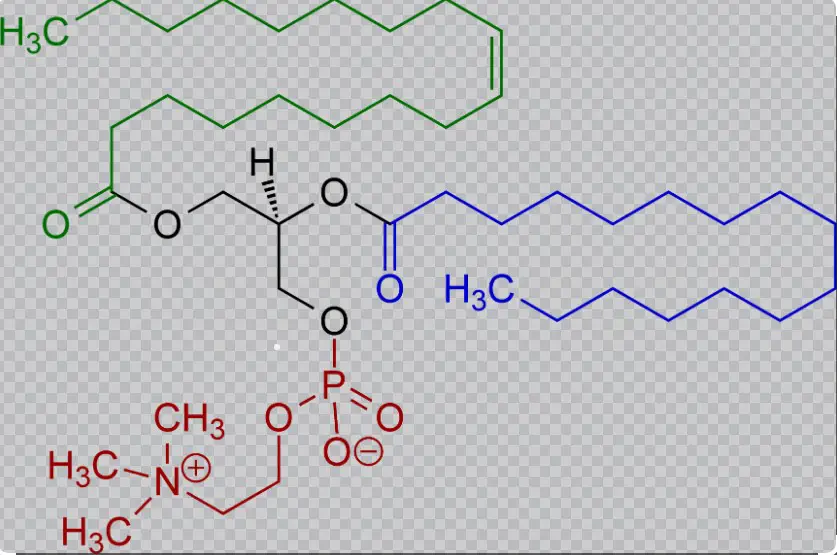
Phosphatidylcholine Essentials
Definition and Physiological Importance
Phosphatidylcholine is a compound that forms a significant part of cell membranes, crucial for their integrity and function. It is derived from choline and plays key roles in:
- Cell signaling: Ensures messages are correctly passed between cells.
- Fat metabolism: Helps in the breakdown and distribution of fats.
- Liver health: Prevents fat accumulation in the liver.
Its physiological importance cannot be overstated, as it is vital for the proper functioning of almost every bodily process.
How It’s Derived from Choline
Phosphatidylcholine is synthesized from choline through a biochemical process involving the methylation of phosphatidylethanolamine. This conversion is crucial for the body to utilize choline in supporting cell membrane structure and function.
Dietary Sources
While the body can produce phosphatidylcholine from choline, dietary sources also contribute to its levels:
- Eggs: Again, the yolk is notably rich in phosphatidylcholine.
- Soybeans: Soy lecithin, in particular, is a significant source.
- Meat and fish: Similar to choline, liver and fish are good sources.
- Nuts: Peanuts and almonds provide phosphatidylcholine as well.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help maintain adequate phosphatidylcholine levels.
Key Differences
Chemical Structure and Composition
While choline is a quaternary ammonium compound, phosphatidylcholine is a phospholipid. The difference in their chemical structure is crucial; phosphatidylcholine contains choline as part of its larger molecule, which also includes fatty acids and a phosphate group. This structure makes phosphatidylcholine an essential component of cell membranes.
Biological Functions in the Body
The functions of choline and phosphatidylcholine, while interrelated, have distinct impacts on health:
- Choline is primarily involved in brain health, liver function, and as a methyl donor in various metabolic processes.
- Phosphatidylcholine is crucial for cell membrane integrity, fat metabolism, and in facilitating communication between cells.
Understanding their unique roles helps clarify why both are essential for holistic health.
Nutritional Benefits Comparison
Nutritional benefits of choline and phosphatidylcholine highlight their importance:
- Choline supports cognitive functions, such as memory and mood, aids in fat metabolism, and is vital for DNA synthesis.
- Phosphatidylcholine contributes to maintaining the structural integrity of cells, supports the nervous system, and is beneficial for liver health.
Health Benefits
Choline
Cognitive Health and Brain Development
Choline is essential for the brain’s health and its development, especially during pregnancy and early childhood. It contributes to neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons), myelination (the formation of protective sheaths around neurons), and synaptogenesis (the formation of synapses between neurons). These processes are crucial for learning, memory, and overall cognitive function. Studies suggest adequate choline intake during pregnancy significantly impacts fetal brain development and may reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
Liver Function and Detoxification
Choline plays a pivotal role in liver function, particularly in fat metabolism and the prevention of fatty liver disease. It helps transport fat from the liver to cells throughout the body, preventing fat accumulation that can lead to liver damage. Moreover, choline’s involvement in detoxification processes ensures the removal of harmful substances from the body, protecting the liver from damage and diseases.
Other Significant Benefits
- Heart Health: Choline is involved in homocysteine metabolism, which helps reduce the risk of heart diseases.
- Inflammation: It may help reduce levels of inflammatory markers, contributing to overall health.
- Pregnancy and Lactation: Adequate choline intake is crucial for fetal development and breast milk quality.
Phosphatidylcholine
Membrane Integrity and Cell Signaling
Phosphatidylcholine is vital for the structural integrity of cell membranes, ensuring they remain flexible and functional. This flexibility is crucial for cell signaling, the process by which cells communicate with each other to carry out various biological functions. By maintaining membrane structure, phosphatidylcholine supports the body’s overall health and the efficiency of cellular processes.
Role in Lipid Metabolism
This compound is also essential in lipid metabolism, facilitating the breakdown and transport of fats and cholesterol in the body. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and supporting liver health. By ensuring fats are efficiently metabolized, phosphatidylcholine helps prevent the accumulation of fats in the liver, contributing to the prevention of fatty liver disease and other metabolic conditions.
Contribution to Mental Health
Phosphatidylcholine has been shown to contribute to mental health, with implications for managing depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. As a component of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in memory and learning, phosphatidylcholine supplementation may improve symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia.
Potential Side Effects
Overconsumption Risks of Choline
While choline is essential, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as a fishy body odor, sweating, gastrointestinal distress, and in severe cases, hypotension (low blood pressure). The risk of cardiovascular disease may also increase with very high intakes of choline due to the conversion of choline into trimethylamine by gut bacteria, which is then converted into trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a substance linked to heart disease.
Phosphatidylcholine Supplementation Concerns
Similarly, while phosphatidylcholine supplements can be beneficial, they are not free from potential side effects. These can include gastrointestinal upset, diarrhea, and nausea, particularly at high doses. It’s important for individuals considering phosphatidylcholine supplements to consult with healthcare providers to ensure safe and appropriate use.
Dietary Recommendations
Optimal Sources of Choline and Phosphatidylcholine
To meet the recommended intakes, incorporating a variety of foods rich in choline and phosphatidylcholine is key. These include:
- Eggs (particularly the yolk)
- Meat (liver and other organ meats are particularly high in choline)
- Fish
- Soybeans and soy products (a good source of phosphatidylcholine)
- Nuts and seeds
- Vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts
Integrating These Nutrients into Your Diet
Incorporating choline and phosphatidylcholine into your diet can be simple with some planning. Consider:
- Starting your day with an egg-based breakfast.
- Including a serving of lean meat, fish, or soy products in your meals.
- Snacking on nuts or adding them to salads and dishes.
- Ensuring a variety of vegetables are part of your daily diet.
FAQs
What is Choline?
Choline is an essential nutrient that supports various bodily functions, including cellular growth, metabolism, and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. It’s crucial for brain health, liver function, and even muscle movement. The body can produce choline, but not in sufficient amounts, making dietary intake necessary.
How does Phosphatidylcholine differ from Choline?
Phosphatidylcholine is a derivative of choline that primarily forms part of cell membranes, ensuring their structural integrity and facilitating cell signaling. Unlike choline, phosphatidylcholine has specific roles in fat metabolism and liver health, showcasing a more targeted function within the body.
Can you get enough Choline and Phosphatidylcholine from diet alone?
Yes, it is possible to obtain sufficient amounts of both choline and phosphatidylcholine through a balanced diet rich in eggs, lean meats, fish, nuts, and certain vegetables. However, some individuals, such as pregnant women or those with specific genetic variations, may require supplementation to meet their needs fully.
Are there any side effects of taking Phosphatidylcholine supplements?
While phosphatidylcholine supplements are generally safe for most people, excessive intake can lead to side effects such as sweating, stomach issues, and diarrhea. It’s important to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
In summarizing the key differences and health impacts of choline and phosphatidylcholine, it’s clear that both nutrients hold indispensable roles in human health. Their distinct but complementary functions highlight the importance of a well-rounded diet or carefully chosen supplementation to support overall wellness. By recognizing and respecting the unique contributions of choline and phosphatidylcholine, individuals can make informed decisions about their nutritional intake, ultimately paving the way for optimal health and longevity.
Fostering an understanding of these nutrients not only aids in achieving dietary balance but also underscores the complexity of nutritional science. As research continues to unveil the nuanced roles of choline and phosphatidylcholine, the potential for improved health outcomes through targeted nutrition becomes ever more apparent, emphasizing the need for public awareness and education on this topic.