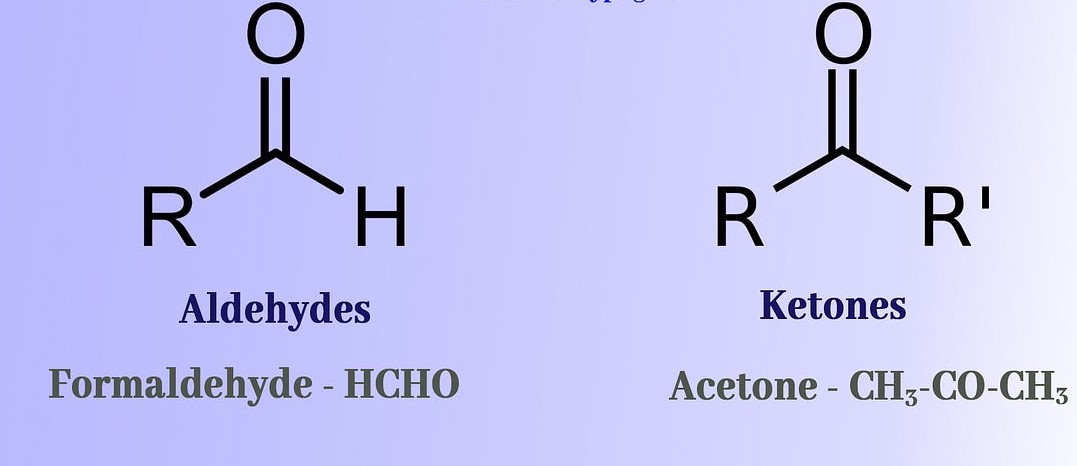
Carbonyl and ketone are two distinct organic compounds that share some common characteristics. However, there are also key differences between the two that are important to understand. In this blog, we will explore the differences between carbonyl and ketone and discuss how they interact with other compounds.
By understanding the differences between these two compounds, we can better appreciate the complexity of organic chemistry.
Structure of carbonyls and ketones
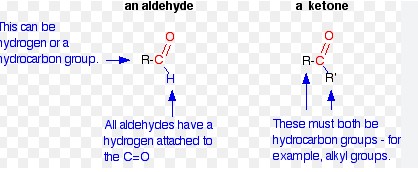
Carbonyls and ketones are two distinct types of organic compounds, and while they have some similarities, they also have some marked differences. Carbonyls are compounds that contain a carbon-oxygen double bond, and can be divided into two categories: aldehydes and ketones.
Aldehydes possess a hydrogen atom attached to the carbon-oxygen double bond, whereas ketones lack a hydrogen atom and instead have two alkyl groups or an aromatic group attached to the carbon-oxygen double bond. Therefore, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones, and the double bond in aldehydes is more susceptible to attack by nucleophiles. In addition, aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids, whereas ketones cannot.
All in all, the differences between carbonyls and ketones can be summarized as follows: aldehydes have a hydrogen atom attached to the carbon-oxygen double bond, while ketones lack such a hydrogen atom. Additionally, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones, and can be oxidized to carboxylic acids, whereas ketones cannot.
Reactivity and nomenclature of carbonyls and ketones
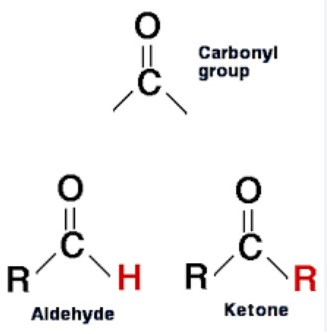
Carbonyls and ketones are two closely related classes of organic compounds that can be distinguished by the presence of a carbon-oxygen double bond (carbonyl group). Carbonyls, such as aldehydes and ketones, contain functional groups with the general formula R-C=O.
This difference in structure leads to a difference in reactivity. Carbonyls are more reactive and undergo a range of reactions such as oxidation, nucleophilic substitution and addition, while ketones are much more stable and are not as prone to undergo these types of reactions.
Additionally, ketones have a higher boiling point than carbonyls and are often used as solvents. The nomenclature of these compounds also differs as aldehydes are named using the suffix “-al” while ketones are named using the suffix “-one”.
Synthesis of carbonyls and ketones
Carbonyls and ketones are both organic molecules, and they share many similarities. However, there is a key difference between the two that makes them distinct. The main difference between carbonyls and ketones is the presence of a double bond between the carbon atom and the oxygen atom in a carbonyl, while a ketone only contains a single bond.
This single bond makes a ketone less reactive than a carbonyl, as the oxygen atom in a ketone is less electron-rich than the oxygen atom in a carbonyl. As a result, ketones are more stable compounds and are generally easier to synthesize than carbonyls.
Uses of carbonyls and ketones
Carbonyls and ketones are both organic compounds that contain a carbon-oxygen double bond. While they have similar structures, there are some distinct differences between them.
Carbonyl compounds are characterized by the presence of a carbon-oxygen double bond, and a single hydrogen atom attached to the carbon. Ketones, on the other hand, have two alkyl or aryl groups, or one of each, attached to the carbon atom in the carbonyl group. This gives them a different chemical and physical properties than carbonyls.
For example, ketones are generally more polar and have higher boiling points than carbonyls. Additionally, carbonyls are more reactive than ketones, making them useful for various chemical reactions.
Summary of the difference between carbonyl and ketone
The difference between a carbonyl and a ketone may seem small, but it is an important distinction to make when understanding organic chemistry. In the simplest terms, a carbonyl is a functional group with a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. A ketone, on the other hand, is an organic compound whose structure contains a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms.
A ketone, on the other hand, is an organic compound whose structure contains a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. In other words, ketones are a subset of carbonyls. The most common carbonyl is the Aldehyde, which is an organic compound containing a carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen atom.
As a result, all aldehydes are ketones, but not all ketones are aldehydes.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between carbonyl and ketone can be summarized as follows: Carbonyl is a functional group that contains a carbon-oxygen double bond, while ketones are molecules that contain a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Carbonyl compounds can be either aldehydes or ketones, with the former having at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group, and the latter having two carbon atoms attached to the carbon of the carbonyl group. Carbonyl compounds are highly reactive due to their electron-rich nature, and ketones are generally less reactive than aldehydes due to the extra carbon atoms that act as electron-withdrawing groups.
Carbonyl compounds are highly reactive due to their electron-rich nature, and ketones are generally less reactive than aldehydes due to the extra carbon atoms that act as electron-withdrawing groups.