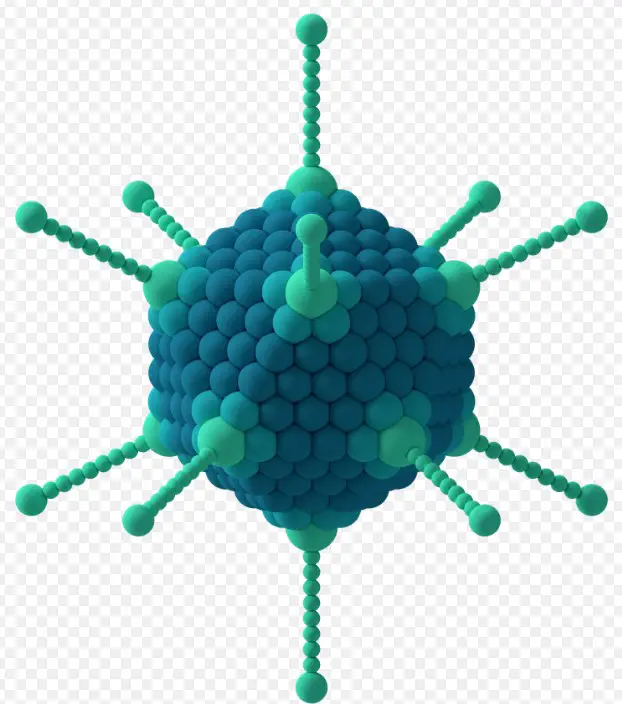
Viruses, those microscopic entities straddling the line between the living and non-living, are marvels of biological architecture. At the heart of their structure lies the capsid, an essential protein shell that encases the viral genome, playing a crucial role in the virus’s ability to infect host cells. Similarly, the capsomere, though less commonly discussed, holds significance as the building block of the capsid, dictating its overall shape and structure.
The difference between a capsid and a capsomere lies primarily in their structural and functional roles within a virus. A capsid is the protein shell surrounding the genetic material of the virus, offering protection and aiding in the infection of host cells. Capsomeres, on the other hand, are the individual protein units that come together to form this protective capsid, with their arrangement determining the capsid’s shape and size.
Understanding these components is not just academic; it holds practical implications for virology, medicine, and biotechnology. The intricate dance between capsid and capsomere shapes how viruses are classified, how they interact with host organisms, and how treatments and vaccines can be developed. Their study illuminates the depths of viral mechanics, offering insights into their lifecycle, the way they hijack host cells, and the possibilities for human intervention.

Viral Architecture
Basic Structure of Viruses
Viruses, at their core, are genetic materials (either DNA or RNA) encased within a protective protein coat known as a capsid. This simple yet effective structure allows viruses to infect host cells by attaching to and entering them, then hijacking their cellular machinery to reproduce. Some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope, adding another layer of complexity to their structure.
Role of the Capsid in Viruses
The capsid plays multiple critical roles in a virus’s life cycle. First and foremost, it protects the viral genetic material from degradation by enzymes and harsh environmental conditions. Secondly, the capsid determines the virus’s specificity; its shape and the receptors on its surface dictate which host cells it can infect. Lastly, in many viruses, the capsid is involved in the delivery of the viral genome into the host cell, facilitating the infection process.
Composition and Function
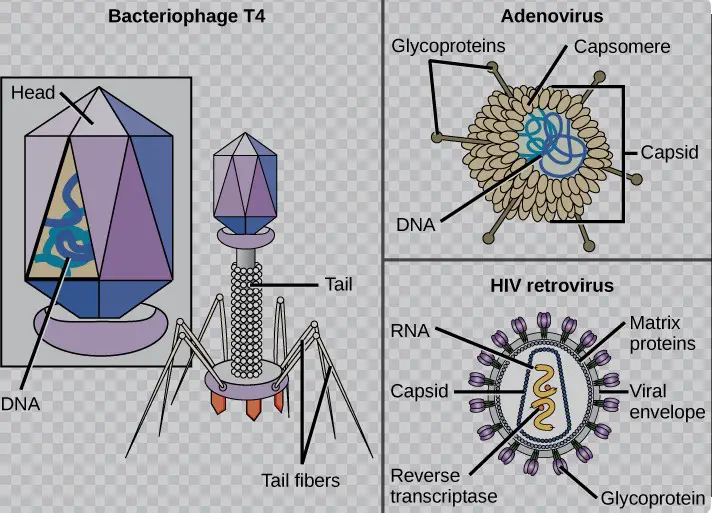
Capsids are made up of protein units called capsomeres. The arrangement of these capsomeres can vary, leading to different capsid shapes such as icosahedral, helical, and complex structures. The specific geometry and composition of the capsid are crucial for the virus’s ability to bind to host cell receptors and are therefore key determinants of infectivity and host range.
Capsid Explained
Definition and Significance
A capsid is the protein shell that encases the viral genome. Beyond its protective role, the capsid influences the infectivity and immunogenicity of the virus. It is the primary interface between the virus and the host’s immune system, making it a target for antiviral drugs and vaccine development.
Types of Capsids
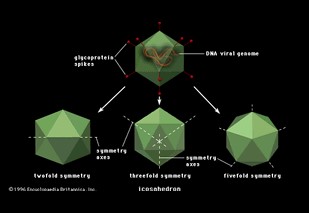
Capsids can be classified into three main types based on their structure: icosahedral, helical, and complex.
- Icosahedral capsids are spherical and made from equilateral triangles, providing a high degree of stability and efficiency in packaging the viral genome.
- Helical capsids form cylindrical shapes, allowing for the accommodation of longer nucleic acids.
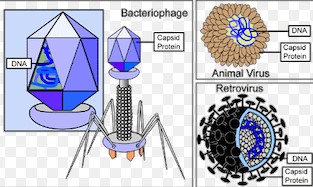
- Complex capsids display a mixture of shapes or additional structures, such as tails in bacteriophages, adapting to specific modes of infection.
Role in Virus Protection and Infection
The capsid’s role extends beyond mere protection; it is instrumental in the virus’s ability to infect host cells. By determining the virus’s shape and structure, the capsid can influence how and where a virus attaches to the host cell, how it releases its genetic material, and ultimately, its success in replicating.
Capsomere Basics
Definition and Characteristics
Capsomeres are the basic building blocks of the capsid. Each capsomere is a protein subunit, and their arrangement on the capsid can be highly symmetrical, contributing to the virus’s overall shape and structural integrity. Capsomeres are critical for capsid assembly during viral replication and can vary widely among different viruses.
Building Blocks of the Capsid
Capsomeres self-assemble to form the capsid in a process that is both specific and efficient, ensuring that viral particles are correctly formed for infection. This self-assembly process is a target for antiviral strategies, aiming to disrupt the formation of new viral particles.
Variability and Composition
The variability in capsomere composition across different viruses contributes to the vast diversity of viral shapes and sizes. This diversity is a direct reflection of the evolutionary pressures faced by viruses as they adapt to infect different host organisms. The composition of capsomeres, including the number and type of proteins, influences not only the capsid’s structure but also its functionality in the viral life cycle.
Capsid vs Capsomere
Structural Differences
The main difference between a capsid and a capsomere lies in their structure. The capsid is the complete protein shell surrounding the viral genome, while capsomeres are the individual protein units that make up this shell. This distinction is crucial for understanding how viruses assemble and infect host cells.
Functional Distinctions
Functionally, the capsid and capsomere serve different purposes. The capsid is involved in protecting the viral genome and facilitating its delivery into host cells. In contrast, capsomeres are primarily concerned with the assembly and structural integrity of the capsid.
Importance in Viral Classification
The structure of the capsid, determined by the arrangement of capsomeres, is a key factor in viral classification. Different arrangements lead to different capsid shapes, which in turn can affect the virus’s infectivity, host range, and immune system evasion strategies. Understanding these differences is essential for the development of antiviral therapies and vaccines, making the distinction between capsid and capsomere a fundamental aspect of virology.
Biological Significance
Capsid and Capsomere in Virus Lifecycle
The lifecycle of a virus is a fascinating process, intricately dependent on the functionality of the capsid. From the moment a virus attaches to a host cell, the capsid’s structure plays a crucial role in facilitating entry. Once inside, the capsid ensures the viral genome’s safe delivery to the site of replication. Capsomeres, by assembling into the capsid, not only protect the genetic material during these stages but also assist in the budding process as new viral particles are formed. This cyclical role underlines the essential nature of capsid and capsomere interactions in viral reproduction.
Impact on Host Cells
The impact of viruses on host cells is predominantly dictated by the capsid’s interaction with the cell. This interaction can trigger immune responses, lead to cell death, or allow the virus to remain dormant within the cell for extended periods. The specificity of this interaction, guided by the capsid’s structure, determines the virus’s ability to infect particular cell types, making it a key factor in the pathogenicity of viral diseases.
Role in Vaccine Development
Understanding the capsid’s role in the virus lifecycle has pivotal implications for vaccine development. Vaccines often use attenuated viruses or viral proteins to stimulate the immune system without causing disease. The capsid proteins, being highly immunogenic, can be targeted to develop vaccines that elicit strong immune responses, providing protection against specific viruses. The detailed study of capsid structures is thus essential for creating effective and safe vaccines.
Visual Comparison
Illustrative Examples
Visual aids and illustrative examples play a significant role in understanding the complex structures of capsids and capsomeres. Diagrams and models can help elucidate the arrangement of capsomeres within a capsid, showcasing how this structure determines the virus’s overall shape and infectivity.
Differences in Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy has been instrumental in distinguishing the detailed structures of capsids and capsomeres. Through this technique, scientists can observe the precise arrangement of capsomeres, revealing patterns that are not visible through other imaging methods. This has led to significant advancements in our understanding of viral structures, highlighting the varied geometries and complexities of capsid assembly.
Evolutionary Perspective
Evolution of Capsid and Capsomere Structures
The evolution of capsid and capsomere structures is a testament to the adaptability and survival strategies of viruses. Over millions of years, viruses have evolved capsids that allow them to efficiently infect host cells, evade immune responses, and transmit between hosts. This evolutionary process has resulted in a diverse array of viral forms, each optimized for its specific environment and host. The study of these structures provides insights into viral evolution, adaptation, and the ongoing arms race between viruses and their hosts.
Adaptive Significance in Different Environments
The adaptive significance of capsid and capsomere structures cannot be overstated. In different environments, the structural features of the capsid enable viruses to withstand varied physical and chemical conditions, ensuring their survival and transmission. For instance, the rugged icosahedral structure of many capsids is particularly suited to resisting degradation outside a host, facilitating the transmission of viruses through environments that would otherwise destroy them.
Research and Technological Applications
Studies on Capsid and Capsomere
Research into capsid and capsomere structures has opened new avenues in virology, molecular biology, and medicine. Studies focusing on the assembly, dynamics, and functionality of these structures have led to a deeper understanding of viral mechanisms, paving the way for innovative treatments and diagnostic tools.
Advances in Virology and Medicine
The advances stemming from capsid and capsomere research have been significant. From the development of antiviral drugs that disrupt capsid assembly to the creation of vaccine platforms based on capsid proteins, the impact on medicine has been profound. These achievements underscore the importance of basic scientific research in driving forward medical innovations.
Future Directions in Research
Looking ahead, the research into capsid and capsomere structures is poised to continue yielding groundbreaking discoveries. Future directions may include the development of nano-scale delivery systems for gene therapy, using engineered capsids to safely and efficiently deliver therapeutic genes to specific cells. Moreover, the ongoing study of viral evolution will enhance our ability to predict and prevent future viral outbreaks, safeguarding public health against emerging viral threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Capsid?
A capsid is the outer protein coat of a virus, providing essential protection for the viral genetic material and playing a pivotal role in the virus’s ability to infect host cells. Composed of protein subunits called capsomeres, the capsid’s structure is critical for the virus’s survival and efficacy in the replication process.
How Do Capsomeres Function?
Capsomeres serve as the building blocks for the capsid, arranging themselves in precise patterns to create the protective shell around the virus’s genetic material. Their arrangement dictates the overall morphology of the virus, influencing its infectivity and interaction with the host’s immune system. Understanding capsomere functions is key to unlocking the secrets of viral architecture and pathology.
Why is the Study of Capsid and Capsomere Important?
The study of capsid and capsomere structures is crucial for advancing our understanding of viral mechanisms of infection and for developing effective vaccines and therapeutics. By deciphering these structures, scientists can design drugs that inhibit viral assembly or enhance the immune response against them, offering new pathways in the fight against viral diseases.
Can Capsid Structure Influence Vaccine Development?
Yes, the structure of the capsid can significantly influence vaccine development. By targeting specific capsid proteins, scientists can create vaccines that prompt the immune system to recognize and attack the virus. The detailed understanding of capsid architecture is thus fundamental for the design of effective vaccines and antiviral therapies.
Conclusion
The intricate world of viruses, with its complex interplay between capsids and capsomeres, offers a fascinating glimpse into the mechanisms of infection and immunity. The distinction between these two components is not just a matter of semantics but a cornerstone of virology that impacts everything from virus classification to the development of antiviral drugs and vaccines. As we continue to explore the depths of viral structures, the knowledge gleaned promises new strategies in our ongoing battle against viral diseases.
Understanding the nuances between a capsid and a capsomere shines a light on the broader complexities of viral life cycles and human intervention efforts. This exploration not only enriches our grasp of viral biology but also underscores the importance of meticulous research in paving the way for medical breakthroughs and effective treatments. In the intricate dance of infection and immunity, every detail matters—down to the smallest protein shell.