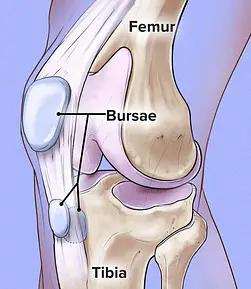
Joint health is crucial for maintaining an active and pain-free lifestyle, particularly as we age. Two lesser-known but vital components in this realm are the bursa and synovial fluid. Both play significant roles, yet they are often overlooked until problems arise.
The bursa and synovial fluid serve distinct but complementary functions within our joints. Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs that provide a cushion between bones and tendons or muscles around a joint, reducing friction. Synovial fluid, on the other hand, is a viscous, egg white-like liquid that fills the cavities of synovial joints, offering lubrication and nutrient distribution to maintain joint health.
These components are integral to our mobility and comfort, performing essential functions that allow our joints to move smoothly under stress. The bursa minimizes the friction from muscle movements, while synovial fluid ensures that our joints are well-lubricated and protected from wear and tear.
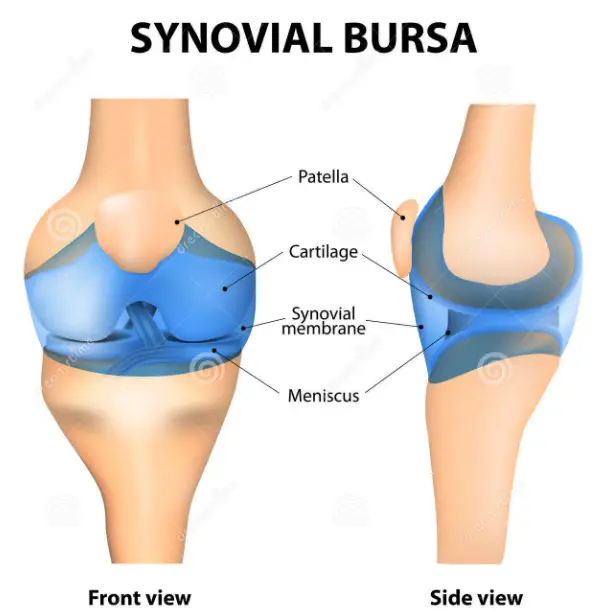
Bursa Explained
Definition and Function
The bursa is a small sac filled with lubricating liquid, situated in areas of the body where tissues could otherwise rub painfully against each other, such as between tendons and bones. Its primary function is to reduce friction and cushion the pressure points, making movement smoother and less painful.
Types of Bursae
There are two main types of bursae found in the human body: synovial bursae and adventitial bursae. Synovial bursae are located between bones and soft tissues and have a direct link to joint cavities, thereby enhancing their efficiency in reducing friction. Adventitial bursae, however, develop in response to stress, and are often found in areas subjected to frequent pressure but not originally equipped with bursae.
Role in Movement
Bursae play a crucial role in facilitating movement by preventing the wear and tear of joints during repetitive motions. By cushioning joints and reducing friction, bursae help maintain joint health and extend the functional life of the joints. This function is vital for both daily activities and in preventing overuse injuries in athletes and individuals with physically demanding jobs.
Synovial Fluid Detailed
Composition and Properties
Synovial fluid is a thick, slippery fluid that is found within the synovial joints. Composed primarily of hyaluronic acid and lubricin, proteins that provide viscosity and elasticity, this fluid is crucial for the proper functioning of joints. The fluid’s sticky nature allows it to lubricate the joint, reducing friction and wearing down of the cartilage.
Functions in Joints
Synovial fluid serves several vital functions in joint health:
- Lubrication: It reduces the friction between the cartilage and other tissues in the joint during movement.
- Shock Absorption: It acts as a cushion against physical impact, protecting the joint from stress and damage.
- Nutrient Distribution: It circulates nutrients from the bloodstream to the cartilage, aiding in repair and maintenance.
Synthesis and Regulation
The synovial membrane, which lines the joint capsules, is responsible for the synthesis of synovial fluid. The production and composition of synovial fluid are influenced by various factors including mechanical stress and inflammatory cytokines, ensuring that the fluid’s properties are responsive to the needs of the joint under different conditions.
Comparing Structures
Physical Differences
While both bursae and synovial fluid are involved in joint lubrication, they differ significantly in structure. Bursae are sac-like structures that provide padding and reduce friction in specific areas. Synovial fluid, in contrast, is a free-flowing liquid that fills the entire joint cavity for widespread lubrication.
Locations and Interactions
Bursae are typically found at points of potential friction such as between skin and bone or between tendons and bones, whereas synovial fluid is present within all synovial joints, surrounding the articulating bones.
Functional Distinctions
Lubrication vs. Cushioning
Though both structures help in joint lubrication, their primary roles differ:
- Bursae: Mainly provide cushioning and reduce direct stress on tissues.
- Synovial Fluid: Primarily reduces friction between cartilages during joint movements.
Healing and Injury Response
The healing processes for injuries to bursae and synovial membranes also differ:
- Bursae: Inflammation of bursae, known as bursitis, typically requires rest, ice application, and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
- Synovial Fluid: Joint injuries involving synovial fluid, such as synovitis, may require more complex interventions, including medication to reduce inflammation and physical therapy to restore function.
Clinical Relevance
Common Disorders
Bursae and synovial fluid are crucial in joint function, but they are also susceptible to various disorders that can impair mobility and cause significant pain. Bursitis, an inflammation of the bursa, frequently affects the shoulder, elbow, and hip joints. Similarly, disorders involving synovial fluid, such as synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membrane) or arthritis (characterized by joint inflammation), directly impact joint health.
Diagnostic Approaches
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effectively treating joint disorders. Here are common diagnostic methods used to assess issues related to bursae and synovial fluid:
- Physical Examination: Initial assessment of joint tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
- Imaging Tests: MRI and ultrasound are crucial for visualizing the state of soft tissues and detecting fluid accumulation.
- Aspiration: Extracting fluid from a joint or bursa for laboratory analysis to identify infections or gout.
Treatment Strategies
Treatment of disorders related to bursae and synovial fluid varies based on severity and underlying causes but typically includes:
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to restore mobility and strengthen the muscles surrounding the joint.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgical removal of the affected bursa or correction of the joint may be necessary.
Research and Innovations
Recent Studies
Recent advancements in medical research have shed light on better management and treatment of joint disorders. Studies exploring the molecular composition of synovial fluid have led to innovations in synthetic lubricants that may supplement or replace natural synovial fluid in diseased joints.
Future Directions
Ongoing research is focused on improving the long-term outcomes for patients with joint disorders. Promising areas include:
- Gene Therapy: Potential to deliver genes directly into the joint that can produce anti-inflammatory agents or elements of synovial fluid.
- Biocompatible Materials: Development of new materials that can mimic the function of bursae or synovial fluid, reducing the need for frequent joint replacements.
FAQs
What is a Bursa?
A bursa is a small sac filled with lubricating fluid located between tissues such as bone, muscle, tendons, and skin. Its primary function is to decrease rubbing, friction, and irritation in the joint area.
How is Synovial Fluid Produced?
Synovial fluid is produced by the synovial membrane that lines the joint capsule. This fluid not only lubricates the joint but also provides nutrients to the cartilage, helping it remain healthy and resilient.
Can Bursae Become Inflamed?
Yes, bursae can become inflamed, a condition known as bursitis. This inflammation can cause pain and restrict movement. Bursitis is typically caused by repeated pressure or overuse of the joint.
What Role Does Synovial Fluid Play in Joint Health?
Synovial fluid plays a critical role in joint health by providing lubrication that reduces friction and wear in the joint. It also serves as a shock absorber and transports nutrients to the cartilage.
How Can You Keep Your Joints Healthy?
Maintaining joint health involves regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods. Avoiding excessive repetitive movements and getting adequate rest also helps preserve joint function.
Conclusion
The intricate roles and functions of bursae and synovial fluid underscore their importance in our joint health. Understanding how these components work together helps appreciate the complexity of our body’s mechanisms for maintaining mobility and reducing pain.
Preserving the health of these essential elements through preventative measures and timely treatment of issues ensures long-term joint functionality and overall well-being. Awareness and education about joint care can empower individuals to make choices that enhance their quality of life.