The heart, a marvel of biological engineering, operates through an intricate electrical system that ensures its rhythmical beating. Two key components of this system are the Bundle of His and the Purkinje Fibres, each playing critical roles in the conduction of electrical impulses. Their function is paramount in maintaining the heart’s rhythm and ensuring the effective pumping of blood throughout the body.
The difference between the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres lies primarily in their location, structure, and specific roles within the heart’s electrical conduction system. The Bundle of His is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction. It acts as a pathway for impulses from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles. The Purkinje Fibres, on the other hand, are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, spreading the impulse quickly and efficiently to ensure a coordinated contraction of the ventricles.
Understanding the distinct roles and characteristics of the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres reveals the elegance of the heart’s electrical system. This knowledge not only illuminates the complexities of cardiovascular physiology but also underscores the importance of each component in maintaining heart health and preventing arrhythmias.
Heart’s Electrical Pathway
The heart is not just a muscle; it’s a sophisticated electrical system. At its core, this system ensures that the heart beats in a rhythmic and coordinated manner, pumping blood to all parts of the body. This electrical pathway is essential for the heart’s function, and understanding it can provide insights into how the heart works and what happens when it doesn’t.
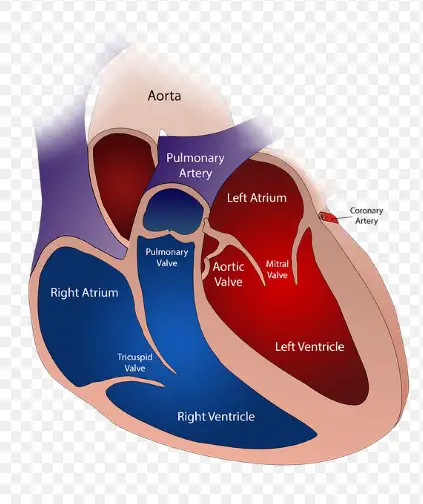
Heart Anatomy
Key Structures Related to Electrical System
The heart’s electrical system involves several key structures:
- SA Node (Sinoatrial Node): Often referred to as the heart’s natural pacemaker, the SA node generates electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat.
- AV Node (Atrioventricular Node): This acts as a gate that slows the electrical signal before it enters the ventricles, ensuring that the heart’s upper and lower chambers beat in sync.
- Bundle of His: A pathway for electrical signals to travel from the AV node to the ventricles.
- Purkinje Fibres: These fibers distribute the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood.
Each of these structures plays a vital role in the heart’s electrical conduction system, coordinating the heart’s beating pattern.
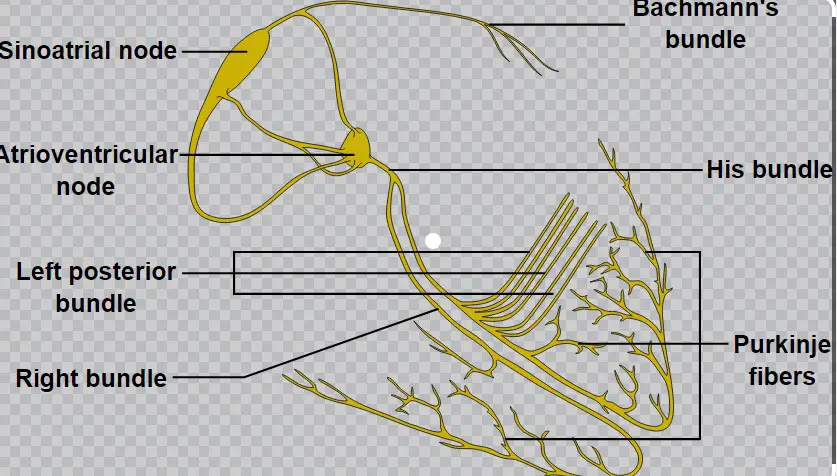
Electrical Conduction System
Role in Heart Rhythm
The electrical conduction system’s main role is to maintain the heart’s rhythm and ensure that blood is pumped efficiently throughout the body. Here’s how it works in steps:
- The SA node fires an electrical impulse, causing the atria to contract.
- This impulse reaches the AV node, where it pauses shortly.
- It then travels down the Bundle of His, dividing into left and right pathways.
- The impulse finally spreads through the Purkinje Fibres, stimulating the ventricles to contract.
This precise sequence ensures the heart beats in a coordinated manner, maintaining a steady flow of blood.
Bundle of His
Definition and Function
The Bundle of His is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction. It forms the electrical bridge between the atria and the ventricles.
Location
This structure is found in the heart’s septum, the wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart. It starts at the AV node and extends into the ventricles.
Structure
The Bundle of His is composed of specialized cardiac muscle fibers. It divides into two main branches: the left and right bundle branches, which further split into finer fibers throughout the ventricles.
Function
The primary role of the Bundle of His is to transmit electrical impulses from the AV node to the ventricles. This ensures that the ventricles contract at the right time, pumping blood to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Purkinje Fibres
Definition and Purpose
Purkinje Fibres are a network of fast-conducting cells that spread the electrical impulse through the ventricles. They ensure a rapid and coordinated contraction.
Location
These fibers are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, branching out from the Bundle of His.
Structure
Purkinje Fibres are unique in their appearance, with a larger diameter and fewer contractile fibers than typical cardiac muscle cells. This allows for the fast transmission of electrical impulses.
Function
The function of the Purkinje Fibres is crucial for the heart’s rhythm. They distribute the electrical impulse efficiently across the ventricles, ensuring a synchronized contraction. This is vital for the effective pumping of blood.
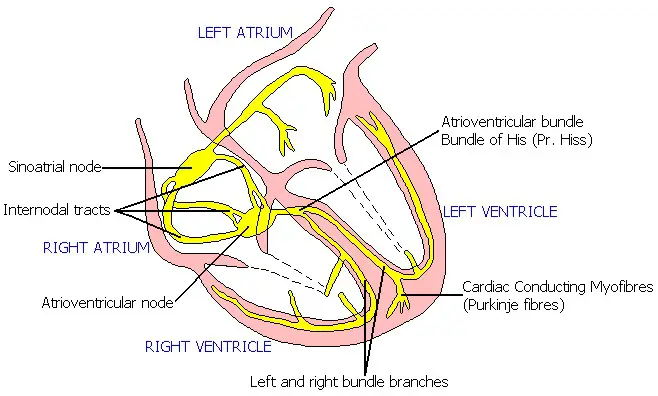
Key Differences
Understanding the distinctions between the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres is crucial for comprehending their roles in the heart’s electrical conduction system. These differences are not just academic; they are vital for diagnosing and treating heart conditions.
Anatomical Position
The Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres differ significantly in their locations within the heart, which impacts their function in the heart’s electrical system.
- Bundle of His: It is located at the upper part of the interventricular septum, directly after the AV node. It acts as the only electrical connection between the heart’s atria and ventricles.
- Purkinje Fibres: These fibers spread out from the left and right branches of the Bundle of His throughout the ventricular myocardium. Their network is extensive, covering the inner ventricular walls.
Structural Features
The physical makeup of the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres reflects their specialized functions in electrical conduction.
- Bundle of His: This structure is composed of compact, specialized cardiac muscle fibers. These fibers are thinner than those of the Purkinje system but are crucial for the precise transmission of electrical signals to the ventricles.
- Purkinje Fibres: Characterized by their unique, large, pale cells with fewer contractile elements, these fibers are designed for rapid electrical transmission. This structure allows for the efficient spread of impulses across the ventricles.
Electrical Conduction Role
The role of these components in the heart’s electrical pathway highlights their importance in ensuring a coordinated heartbeat.
- Bundle of His: It plays a pivotal role in transmitting the electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, acting as a vital bridge in the heart’s conduction system.
- Purkinje Fibres: These fibers facilitate the fast spread of impulses within the ventricles, ensuring a synchronized contraction that is crucial for efficient blood pumping.
Significance in Heart Health
Understanding the differences between the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres is not just academically interesting; it has profound implications for heart health.
- Precision in Diagnosis: Recognizing these differences aids clinicians in pinpointing the exact location of electrical conduction issues, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
- Tailored Treatments: Knowledge of these structures allows for the development of targeted treatments, including pacemaker placement and medication adjustments, to address specific conduction problems.
Role in Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias, or abnormal heart rhythms, often arise from issues in the electrical conduction system. The role of the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres in these conditions is significant.
- Bundle of His Abnormalities: Problems here can lead to blockages in the electrical pathway, resulting in bradycardia (slow heart rate) or complete heart block.
- Purkinje Fibres Dysfunction: Abnormalities can cause ventricular fibrillation, a life-threatening condition where the heart beats rapidly and erratically.
Diagnostic and Treatment Implications
The understanding of how the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres differ has crucial implications for the diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions.
- Electrophysiological Studies: These studies can map the heart’s electrical activity, identifying whether disruptions occur in the Bundle of His or the Purkinje system.
- Treatment Strategies: Depending on the location of the issue, treatment might involve medication to adjust the heart’s rhythm, pacemaker insertion to bypass electrical blockages, or ablation therapy to correct arrhythmias.
FAQs
How do the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres function?
The Bundle of His bridges the gap between the heart’s atria and ventricles, conducting electrical impulses from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles. The Purkinje Fibres, emanating from the Bundle of His, spread these impulses rapidly across the ventricles, ensuring their simultaneous contraction for effective blood pumping.
What happens if the Bundle of His or Purkinje Fibres malfunction?
Malfunction in either the Bundle of His or the Purkinje Fibres can lead to arrhythmias, affecting the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently. Symptoms may include palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, or in severe cases, sudden cardiac death. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for managing these conditions.
Can the damage to the Bundle of His or Purkinje Fibres be repaired?
Currently, direct repair of the Bundle of His or Purkinje Fibres is not possible. However, treatments such as pacemakers can help manage the symptoms by ensuring the heart maintains a regular rhythm, compensating for the impaired conduction system.
Why are the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres important in diagnosing heart conditions?
Their crucial roles in the heart’s electrical conduction system make the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres important in diagnosing heart conditions. Abnormalities in their function can be indicative of various cardiac issues, guiding healthcare professionals in identifying and treating arrhythmias and other heart diseases.
Conclusion
The precise orchestration of the heart’s rhythm hinges on the seamless operation of its electrical system, with the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres playing central roles. Their ability to conduct electrical impulses ensures the heart beats in a synchronized manner, highlighting the importance of understanding these components for heart health. Recognizing the differences between them not only aids in the diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions but also marvels at the complexity of human physiology.
In the grand tapestry of the cardiovascular system, the Bundle of His and Purkinje Fibres stand out for their indispensable roles in maintaining life. Their study not only enriches our knowledge of cardiac function but also emphasizes the beauty and complexity of the human body, inspiring further research and innovation in heart health and treatment.