Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone pivotal to pregnancy tests and fertility treatments, yet its variant, Beta HCG, often emerges in discussions with little clarity on its distinction. This hormone’s presence and levels in the body can signal a range of conditions, from the confirmation of pregnancy to the diagnosis of certain types of cancer. The subtle yet significant differences between HCG and Beta HCG are essential for medical diagnostics, affecting both interpretation and outcome.
Beta HCG refers specifically to the beta subunit of the Human Chorionic Gonadotropin hormone, which is unique and distinct from the more general HCG marker. This specificity makes Beta HCG a crucial tool in early pregnancy detection and in monitoring certain medical conditions. Unlike the broader HCG tests, which can sometimes yield false positives due to the presence of similar hormones, Beta HCG provides a higher degree of accuracy and reliability in results.
Understanding the nuances between Beta HCG and HCG is vital for anyone navigating pregnancy concerns, fertility treatments, or specific medical diagnoses. The differentiation lies in their molecular structure, usage in diagnostics, and levels of sensitivity to various conditions. This knowledge not only aids in accurate medical assessment but also provides peace of mind to those awaiting critical test results.
Hcg Explained
Definition and Function
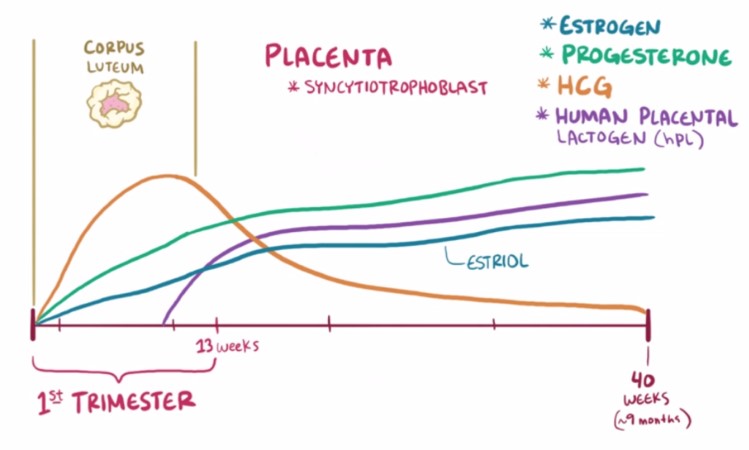
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG) is a hormone produced during pregnancy. It is made by cells formed in the placenta, which nourishes the egg after it has been fertilized and becomes attached to the uterine wall. The primary function of HCG is to support the corpus luteum. This support helps maintain the production of progesterone, a critical hormone for pregnancy.
Role in Pregnancy
During pregnancy, HCG levels increase rapidly, doubling approximately every 72 hours in the first few weeks. This rise in HCG signals the body to keep producing progesterone, thereby preventing menstruation and sustaining the uterine lining. This makes HCG a key marker for pregnancy tests, as its presence indicates that the body is preparing to support a developing fetus.
Beta Hcg Uncovered
Specificity of Beta Hcg
Beta HCG refers to the beta subunit of the Human Chorionic Gonadotropin hormone. This subunit is unique to the HCG hormone, distinguishing it from other similar hormones in the body. The specificity of Beta HCG makes it an invaluable tool in medical diagnostics, especially for early pregnancy detection.
Importance in Early Pregnancy
In early pregnancy, monitoring Beta HCG levels provides crucial information about the viability of the pregnancy. Rising levels typically indicate a healthy pregnancy, while declining or plateauing levels may signal a problem. This specificity and sensitivity to changes make Beta HCG an essential marker in early pregnancy monitoring.
Key Differences
Chemical Structure
HCG is a glycoprotein composed of an alpha and a beta subunit. The alpha subunit is identical to that of other hormones like LH, FSH, and TSH. However, the beta subunit (Beta HCG) is unique to HCG, providing a target for specific diagnostic tests. This distinction in chemical structure is pivotal in the specificity of Beta HCG tests.
Diagnostic Uses
Both HCG and Beta HCG are used in pregnancy tests, but Beta HCG tests are considered more reliable for early pregnancy detection. Due to its specificity, Beta HCG is also used in certain medical conditions to diagnose and monitor treatment for gestational trophoblastic diseases and some cancers.
Sensitivity Levels
Beta HCG tests are highly sensitive, capable of detecting small amounts of the hormone. This sensitivity makes them particularly useful for early detection of pregnancy, sometimes as early as seven to nine days post-conception, before a missed period.
Diagnostic Applications
Pregnancy Testing
Role of HCG and Beta HCG
In pregnancy testing, both HCG and Beta HCG play pivotal roles. However, Beta HCG’s specificity to the beta subunit allows for earlier detection of pregnancy, making it a preferred marker in clinical settings.
Comparing Test Accuracies
- HCG tests can detect pregnancy about 11 to 14 days after conception.
- Beta HCG tests can detect pregnancy as early as 7 to 9 days after conception, offering a quicker indication of pregnancy.
This difference highlights the enhanced sensitivity and accuracy of Beta HCG tests in early pregnancy detection.
Fertility Treatments
Monitoring Beta Hcg Levels
In fertility treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), monitoring Beta HCG levels is critical. Increasing levels after treatment indicate successful implantation and the start of pregnancy. This monitoring helps in making informed clinical decisions about the next steps in patient care.
Guiding Clinical Decisions
- Early detection of pregnancy allows for timely interventions if needed.
- Helps in assessing the health and development of the pregnancy.
- Guides decisions regarding medication and care plans.
Tumor Markers
Beta Hcg in Oncology
Beta HCG is also a marker in oncology, particularly for germ cell tumors and some other types of cancer. Elevated levels can indicate the presence of tumors, aiding in diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Distinguishing Between Types
- Testicular cancer often shows elevated Beta HCG levels.
- Ovarian and other cancers can also elevate Beta HCG, but less commonly than testicular cancer.
- Monitoring changes in Beta HCG levels can help in tracking tumor response to treatment.
Testing Procedures
Blood Tests
Process and Interpretation
Blood tests for HCG and Beta HCG are common procedures used in medical diagnostics, especially for confirming pregnancy and monitoring certain health conditions. The process involves drawing a small amount of blood, usually from the arm, and analyzing it in a laboratory to measure the levels of HCG or specifically the beta subunit, Beta HCG.
- Collect Blood Sample: A healthcare provider draws blood from a vein.
- Laboratory Analysis: The sample is sent to a lab, where it’s tested for HCG or Beta HCG levels.
- Result Interpretation: High levels of HCG or Beta HCG can confirm pregnancy, with Beta HCG offering a more specific indication. Additionally, changes in these levels over time can provide important diagnostic information.
Beta HCG vs. HCG Levels
While both HCG and Beta HCG tests measure aspects of the same hormone, Beta HCG tests are more specific and sensitive. This specificity is crucial for early pregnancy detection and in diagnosing and monitoring other medical conditions where HCG levels may be elevated.
Urine Tests
Ease of Use
Urine tests for HCG are widely used because of their convenience and accessibility. These tests can be done at home with over-the-counter pregnancy test kits, which detect the presence of HCG in the urine.
- Simple Steps: Apply urine to the test stick and wait for the indicated time.
- Immediate Results: Read the results directly from the test device.
Sensitivity and Specificity
Urine HCG tests are less sensitive than blood tests, usually detecting pregnancy about 12 to 14 days after conception. Their specificity varies, with a small chance of false positives due to factors like the presence of similar hormones or certain medical conditions.
Factors Affecting Levels
Normal Fluctuations
HCG levels can fluctuate significantly, especially in early pregnancy. After implantation, levels rise rapidly, peaking around 10 weeks of gestation before gradually decreasing.
- Double Time: In a healthy pregnancy, HCG levels can double approximately every 48 to 72 hours in the first trimester.
- Plateau and Decline: After reaching a peak, levels plateau and then decline as the placenta takes over hormone production.
Pathological Conditions
Various conditions can affect HCG levels, leading to higher or lower readings than expected.
- Higher Levels: Can indicate multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets), molar pregnancies, or certain types of tumors.
- Lower Levels: May suggest a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
Clinical Significance
Early Pregnancy Detection
HCG tests, especially blood tests measuring Beta HCG, are critical for early pregnancy detection. Detecting pregnancy early can help ensure proper prenatal care and monitor the pregnancy’s viability.
Miscarriage and Ectopic Pregnancy
Abnormal HCG levels can signal complications.
- Decreasing Levels: May indicate a miscarriage.
- Low Levels: Might suggest an ectopic pregnancy, where the embryo implants outside the uterus.
Molar Pregnancies and Trophoblastic Disease
- Significantly Elevated Levels: Can indicate a molar pregnancy, a rare complication where a tumor forms instead of a normal pregnancy.
- Trophoblastic Disease: High levels of HCG can also signal gestational trophoblastic disease, a condition where tumors form in the cells that would normally become the placenta.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of Beta HCG levels in pregnancy?
Beta HCG levels play a crucial role in early pregnancy detection and monitoring. These levels rise significantly in the first trimester, providing a key indicator of pregnancy viability. High or low Beta HCG levels can also signal potential complications, such as ectopic pregnancies or miscarriages, necessitating timely medical intervention.
Can Beta HCG detect tumors?
Yes, elevated Beta HCG levels can indicate the presence of certain tumors, particularly those originating in the testes, ovaries, bladder, pancreas, or the digestive tract. Its role as a tumor marker aids in diagnosing and monitoring treatment efficacy for certain types of cancer, emphasizing the hormone’s importance beyond reproductive health.
How do HCG and Beta HCG tests differ?
HCG tests measure the total presence of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin in the body, which can sometimes include other similar hormones, leading to less specificity. In contrast, Beta HCG tests target the unique beta subunit of the HCG hormone, offering a higher degree of accuracy and specificity for pregnancy testing and certain medical conditions.
Why monitor Beta HCG levels in fertility treatments?
Monitoring Beta HCG levels in fertility treatments helps assess the success of procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF). Increasing Beta HCG levels post-treatment can indicate successful implantation and early pregnancy, guiding further medical care and supporting the emotional and physical journey of those involved.
Conclusion
The differentiation between Beta HCG and HCG marks a significant stride in medical diagnostics, offering precision where general testing falls short. Understanding these differences not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also underscores the hormone’s diverse roles in managing reproductive health and detecting critical conditions. As we navigate through the complexities of human health, the distinction between Beta HCG and HCG serves as a beacon for informed medical decisions, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and peace of mind for patients worldwide.
The importance of accurate, sensitive diagnostics cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to conditions as life-altering as pregnancy and cancer. Armed with the knowledge of what sets Beta HCG apart from its counterpart, both patients and practitioners can approach treatment and monitoring with confidence, ensuring that every decision is informed and every outcome is as positive as possible.