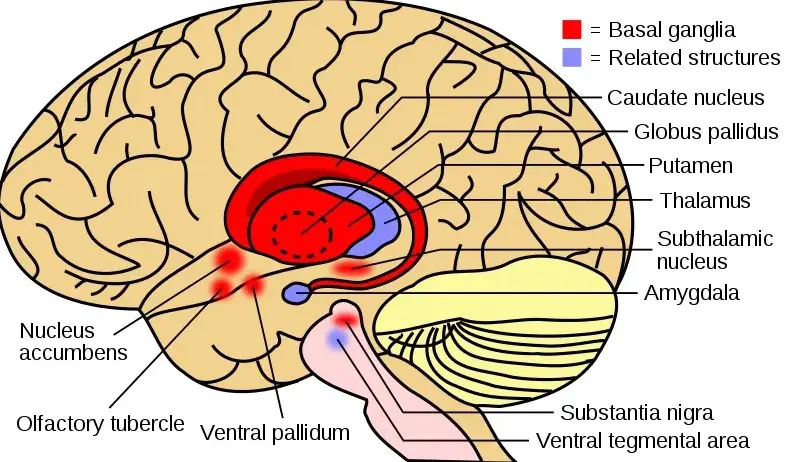
The human brain is incredibly complex, and as such, it is comprised of many different parts. Two of the most important parts are the basal ganglia and cerebellum.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between the basal ganglia and cerebellum in order to better understand their unique functions.
Anatomy and function of the basal ganglia
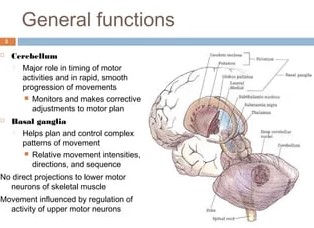
The basal ganglia and the cerebellum are two distinct structures of the brain, each with its own unique anatomy and function. The basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclei located deep within the brain, consisting of the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus, and the substantia nigra. These structures are involved in a variety of processes, including the control of voluntary motor movements, learning and memory, and the regulation of emotions.
The cerebellum, on the other hand, is located in the hindbrain and is involved primarily in the coordination of motor movements and the maintenance of posture and balance. Though both the basal ganglia and the cerebellum are integral for the control of movement, they have different roles in the process.
The basal ganglia are primarily involved in the initiation and execution of movement, while the cerebellum is involved in the coordination, timing, and accuracy of voluntary movement. In other words, the basal ganglia are the “gas pedal,” responsible for initiating and controlling movements, while the cerebellum is the “steering wheel,” responsible for ensuring smooth and accurate movements.
Anatomy and function of the cerebellum
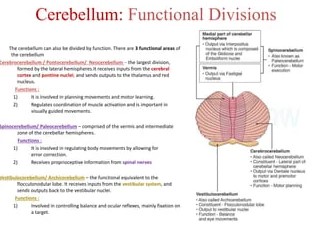
The cerebellum is an integral part of the brain that is responsible for coordination and balance, as well as for influencing cognitive functions. It is located at the back of the head, just above the brain stem, and is made up of two hemispheres that are connected by a thick band of nerve fibers.
It is one of the largest structures in the brain and is composed of a large number of neurons that are arranged in a highly complex manner. While it is often compared to the basal ganglia, there are several differences between the two. The cerebellum is larger, has more neurons, and is involved in more complex functions such as coordination and balance.
Additionally, the basal ganglia is more involved in motor control, while the cerebellum is more involved in cognitive functions such as learning, memory, and decision-making.
Role of the basal ganglia and cerebellum in movement control
The basal ganglia and cerebellum are two important structures in the brain that play a significant role in movement control. While both are responsible for movement, the way in which they each contribute to movement control is quite different. The basal ganglia are largely responsible for the initiation and sequencing of movements, while the cerebellum is in charge of fine-tuning and coordinating those movements.
The basal ganglia are largely responsible for the initiation and sequencing of movements, while the cerebellum is in charge of fine-tuning and coordinating those movements. The basal ganglia are involved in the planning and decision-making of movements, while the cerebellum is responsible for the accuracy and precision of those movements. Simply put, the basal ganglia are responsible for the thought behind the action, while the cerebellum is responsible for the execution of the action.
Difference in pathology between basal ganglia and cerebellum
The basal ganglia and cerebellum are two distinct brain structures with a range of differences in their pathology. The basal ganglia is associated with motor control, cognition, and emotion, while the cerebellum is mainly responsible for motor coordination and fine-tuning of movement. Both regions are linked to various neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Tourette syndrome.
Both regions are linked to various neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and Tourette syndrome. However, the pathology of these diseases can vary greatly depending on which region of the brain is affected. For example, a person with Parkinson’s disease may experience tremors and difficulty with movement, but a person with a cerebellar disorder may experience difficulty with coordination and balance.
By understanding the differences between the two regions, we can better understand the different neurological disorders that affect them.
Clinical impact of differences between basal ganglia and cerebellum
The basal ganglia and the cerebellum are two distinct parts of the brain, and they have a profound impact on our cognitive, motor, and emotional abilities. While both regions play key roles in our neurological health, the differences between them are crucial in understanding their unique functions. The basal ganglia are responsible for initiating and controlling movement, regulating emotions, and learning and memory.
On the other hand, the cerebellum is involved in fine motor control, coordination, and balance. Furthermore, the basal ganglia are also implicated in reward-seeking behavior, while the cerebellum is known to be involved in sensory processing.
Because of these differences between the two, understanding the clinical implications of each is necessary to provide optimal care for patients affected by neurological disorders.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the basal ganglia and cerebellum are two distinct, yet interconnected structures in the brain that play a vital role in motor control and cognition. The basal ganglia is involved in the processing of voluntary movements, as well as the production of emotions, and the maintenance of certain learned behaviors.
While both structures are essential for motor control, they differ in their specific functions and the manner in which they achieve them.