Amphicribral and amphivasal are two terms that are often used when discussing aquatic animals. But what is the difference between them?
We will also discuss how these terms are used to describe different aquatic animals and their habitats. With this information, you will gain a better understanding of these terms and the animals that they describe.
Comparative overview of amphicribral and amphivasal
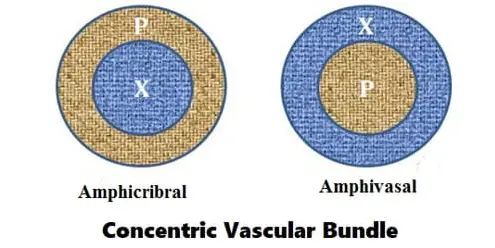
Amphicribral and amphivasal are two distinct categories of organisms, each with its own unique characteristics. While they may appear similar at first glance, they contain distinct physiological, anatomical, and behavioral differences. Amphicribral organisms, such as amphibians, are characterized by having a dual-life cycle, living both in the water and on the land.
They possess aquatic and terrestrial adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive in both environments. Amphivasal organisms, such as fish, are strictly aquatic and are unable to live on land.
They possess adaptations that allow them to survive and thrive in the aquatic environment, such as gills, fins, and a streamlined body shape. The major difference between the two is that amphicribral organisms can exist in both aquatic and terrestrial environments, whereas amphivasal organisms are restricted to the aquatic environment.
The anatomy and physiology of amphicribral and amphivasal
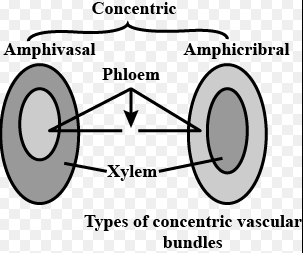
The anatomy and physiology of amphicribral and amphivasal organisms is an interesting study in the differences between two highly specialized forms of life. Amphicribral organisms, such as amphibians, have both an aquatic and a terrestrial lifestyle. They are able to live in and move between both water and land.
They are able to live in and move between both water and land. On the other hand, amphivasal organisms, such as sea turtles, are only able to exist in water but can also move between different areas of a single water body. While both groups share some similar features—such as the ability to breathe through their skin—they have several distinct differences in their anatomy and physiology.
Amphicribral organisms, for example, have a more developed respiratory system, allowing them to utilize their lungs when on land. Amphivasal organisms, on the other hand, have a more advanced circulatory system and specialized organs that allow them to remain submerged for extended periods of time.
Ultimately, these differences are what make these two types of organisms so unique and fascinating.
Behavioral differences between amphicribral and amphivasal
When it comes to the behaviors of amphibians, there are some important differences between amphicribral and amphivasal species. Amphicribral species are generally more active during the day and are found in a variety of wetland habitats.
These amphibians often hide in vegetation or under rocks and logs during the day. Both types of amphibians feed on a variety of insects, worms, and other small animals but amphicribral species may also consume plant material.
In general, amphicribral species are more social, while amphivasal species are more solitary. Additionally, amphicribral species tend to be more vocal than amphivasal species, with some species making a chirping sound during the mating season.
Adaptations of amphicribral and amphivasal to their environment
Amphicribral and amphivasal organisms are two very different creatures, adapted to the environments they inhabit. Amphicribral, such as the axolotl, have both terrestrial and aquatic adaptations, enabling them to move between water and land. Amphivasal organisms, like the mudskipper, are adapted to only one environment and have developed specialized features to cope with their environment.
Amphicribral organisms usually have gills and lungs, as well as specialized structures on their feet, which allow them to move between land and water. Amphivasal organisms, however, only possess gills and are adapted to survive in water.
They may have fins, webbed feet, or specialized scales to help them move in the water.
Conservation of amphicribral and amphivasal
Amphicribral and amphivasal are two different organisms that share many of the same characteristics, but have distinct differences as well. Amphicribral organisms, such as frogs, have the ability to move freely between land and water environments, whereas amphivasal organisms, such as sea turtles, can only move between land and sea. The main differences between these two groups are in the type of locomotion each uses and the habitats they inhabit.
The main differences between these two groups are in the type of locomotion each uses and the habitats they inhabit. Amphicribral organisms, such as frogs, use four-legged locomotion to move on land, while amphivasal organisms, such as sea turtles, use flippers to propel them through the water. Additionally, amphicribral organisms typically inhabit freshwater or terrestrial habitats, while amphivasal organisms inhabit saltwater habitats.
Both groups play an important role in the conservation of aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, but understanding the differences between them is key to protecting them.
Final Touch
Conclusion:In conclusion, the primary difference between amphicribral and amphivasal organisms is their mode of circulation. Amphicribral organisms have a single circulatory system, while amphivasal organisms have two separate circulatory systems.
Both types of organisms have a variety of adaptations and body plans that allow them to survive in their aquatic environment. Each type of organism has its own advantages, disadvantages, and unique characteristics that make it suited for its particular niche. Understanding the differences between these two types of organisms can help us to better appreciate the diversity of life in our oceans and other aquatic environments.