Allyl chloride and vinyl chloride are two chemical compounds that play crucial roles in the chemical industry, each with unique properties and applications. Despite their similar names and containing chlorine, they have distinct molecular structures and uses. This difference not only influences their physical and chemical properties but also determines their applicability in various industrial processes.
The key difference between allyl chloride and vinyl chloride lies in their molecular structures and subsequent applications. Allyl chloride, a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, is used primarily in the synthesis of other chemicals, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. On the other hand, vinyl chloride is a gas at room temperature and serves as a critical precursor in producing polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a versatile plastic used globally.
These compounds’ relevance extends beyond their immediate uses, impacting health, safety, and environmental considerations. Their production, handling, and disposal require careful management to mitigate potential adverse effects, highlighting the importance of understanding their characteristics, applications, and risks. This awareness ensures their beneficial use while safeguarding human health and the environment.
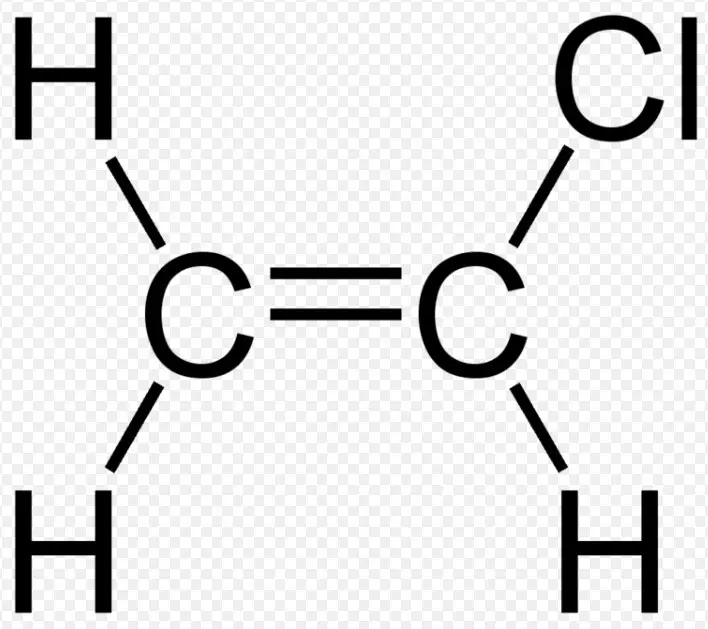
Chemical Structures
Allyl Chloride Overview
Allyl chloride, known by the chemical formula C3H5Cl, stands out due to its unique molecular structure. It consists of a three-carbon chain with a double bond between the first and second carbons, and a chlorine atom attached to the third carbon. This structure grants allyl chloride its reactive properties, making it an essential building block in organic synthesis. The presence of the double bond and the chlorine atom at the terminal carbon is pivotal for its chemical behavior and utility in various reactions.
Vinyl Chloride Overview
Vinyl chloride, with the formula C2H3Cl, presents a simpler structure compared to allyl chloride. It features a two-carbon chain with a single double bond between these carbons, and a chlorine atom attached to one of these. This structure is fundamental for vinyl chloride’s role in polymer chemistry, especially in forming polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a material ubiquitous in modern life. The vinyl group (ethenyl group) is key to its reactivity and application in polymerization processes.
Production Methods
Creating Allyl Chloride
The production of allyl chloride is a critical process in the chemical industry, involving several steps:
- Chlorination of propylene: This primary method involves reacting propylene with chlorine gas in the presence of light or a catalyst. The reaction follows a free radical mechanism, yielding allyl chloride as a major product.
- Purification: The crude allyl chloride is purified through distillation to remove impurities and obtain the compound in high purity.
These steps are essential for producing allyl chloride on an industrial scale, ensuring the availability of this key chemical for further synthesis.
Synthesizing Vinyl Chloride
Vinyl chloride production primarily follows the ethylene dichloride route, a two-step process:
- Chlorination of ethylene: Ethylene reacts with chlorine, producing ethylene dichloride (EDC) in a direct chlorination process.
- Cracking of EDC: Ethylene dichloride is then thermally cracked at high temperatures, yielding vinyl chloride and hydrochloric acid as by-products.
This method is efficient and widely used, underscoring the importance of vinyl chloride in the chemical industry, especially for PVC production.
Physical Properties
Allyl Chloride Properties
Allyl chloride displays several notable physical properties:
- Boiling point: It boils at around 46°C, indicative of its volatility.
- Melting point: Its melting point is -136°C, reflecting its liquid state at room temperature.
- Density: With a density of 0.94 g/cm³, it is slightly less dense than water.
These properties are crucial for handling, storage, and application in chemical synthesis.
Vinyl Chloride Properties
Vinyl chloride’s physical characteristics are distinct:
- Gaseous state: It is a gas at room temperature, with a boiling point of -13.4°C.
- High volatility: This property necessitates careful handling and storage under pressure to maintain it in a liquid state for industrial use.
Understanding these properties is essential for the safe and effective use of vinyl chloride, particularly in PVC production.
Applications
Uses of Allyl Chloride
Allyl chloride finds extensive use in various sectors:
- Pharmaceuticals: It serves as a precursor for active pharmaceutical ingredients.
- Agrochemicals: Used in producing pesticides and herbicides.
- Specialty chemicals: Involved in manufacturing a wide range of chemicals, including intermediates for resins and polymers.
Its versatility stems from its reactive double bond, enabling the synthesis of complex molecules.
Vinyl Chloride in Industry
Vinyl chloride plays a pivotal role in the production of PVC, which finds applications in:
- Construction: For pipes, fittings, and profiles.
- Healthcare: In medical devices and packaging.
- Consumer goods: Including packaging materials, clothing, and toys.
The polymerization of vinyl chloride to produce PVC underscores its importance in modern manufacturing and daily life.
Health and Safety
Allyl Chloride Hazards
Allyl chloride poses several health risks. It is highly flammable and can cause severe irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system when exposed. Prolonged exposure may lead to more serious conditions such as respiratory distress or even chemical burns. To ensure safety, industries employ several measures:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respirators.
- Installation of ventilation systems to reduce airborne concentrations.
- Regular safety training for workers to handle spills and exposures correctly.
Vinyl Chloride Risks
Vinyl chloride is classified as a carcinogen, specifically linked to a rare form of liver cancer known as angiosarcoma. Its risks are not limited to cancer; exposure can also lead to liver, lung, and brain damage. Given these dangers, precautions are paramount:
- Strict monitoring of air quality in workplaces.
- Use of closed systems in manufacturing to minimize worker exposure.
- Implementation of health surveillance programs for early detection of adverse effects.
Environmental Impact
Allyl Chloride and the Environment
The environmental impact of allyl chloride is noteworthy, primarily due to its toxicity to aquatic life. It can cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment if not managed properly. Measures to mitigate these impacts include:
- Tight control of emissions during production and processing.
- Treatment of wastewater before discharge to remove contaminants.
- Development and use of less hazardous alternatives where feasible.
Vinyl Chloride’s Environmental Concerns
Vinyl chloride presents significant environmental challenges, particularly in terms of its persistence and the potential to form dioxins, highly toxic compounds, when burned. The production of PVC also generates waste and by-products that require careful management. Strategies to address these concerns include:
- Strict regulations on emissions and waste management.
- Research into recycling and disposal methods to minimize the environmental footprint.
- Encouraging the use of alternative materials that are less harmful to the environment.
Regulatory Status
Regulating Allyl Chloride
The global regulation of allyl chloride involves various standards and guidelines aimed at protecting worker health and the environment. These regulations often include:
- Threshold limit values (TLVs) for occupational exposure.
- Emission standards to control the release into the air and water.
- Storage and handling guidelines to prevent accidents and environmental spills.
Countries and regions may have specific regulations, but the aim is universally to minimize risk and ensure safe use.
Vinyl Chloride Legislation
The regulation of vinyl chloride is more stringent due to its carcinogenic nature. Laws and regulations governing its use, production, and handling include:
- Occupational safety standards, setting permissible exposure limits to protect workers.
- Environmental protection laws, addressing emissions and waste treatment requirements.
- Public health policies, aimed at minimizing the risk of exposure to the general population.
The comprehensive legal framework ensures that the benefits of using vinyl chloride in products like PVC are balanced against the need to protect health and the environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Allyl Chloride?
Allyl chloride is an organic compound characterized by its colorless appearance and strong odor. It’s primarily used as a building block in the synthesis of other chemicals, including various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Its ability to undergo a wide range of chemical reactions makes it valuable in creating complex molecules needed for these industries.
How is Vinyl Chloride Produced?
Vinyl chloride is produced mainly through the thermal cracking of ethylene dichloride (EDC) in a process that requires precise temperature control. This method efficiently converts EDC into vinyl chloride, which is then polymerized to form polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a material with extensive applications in construction, healthcare, and everyday consumer products.
Why are Allyl Chloride and Vinyl Chloride Regulated?
Both allyl chloride and vinyl chloride are regulated due to their potential health risks. Vinyl chloride, in particular, is classified as a human carcinogen, necessitating strict controls over its production, handling, and exposure levels. Regulations ensure worker safety, environmental protection, and public health by controlling emissions and managing chemical storage and disposal practices.
What are the Environmental Impacts of Vinyl Chloride?
The environmental impact of vinyl chloride includes its potential to contribute to air and water pollution. If released into the environment, vinyl chloride can persist and affect aquatic life and air quality. The production and disposal of PVC, derived from vinyl chloride, also pose significant environmental challenges, including waste management and the release of hazardous by-products.
Conclusion
Allyl chloride and vinyl chloride, despite their similarities in naming and chlorine content, stand apart in their chemical structures, applications, and impact on our world. Their distinct roles underscore the diversity within the chemical industry and the tailored approaches needed to utilize these compounds effectively and safely.
Understanding these differences is paramount for industries relying on these chemicals, ensuring they are used responsibly to minimize health and environmental risks. As the chemical industry continues to evolve, the knowledge and management of such substances will remain critical, reflecting our ongoing commitment to safety, innovation, and sustainability.