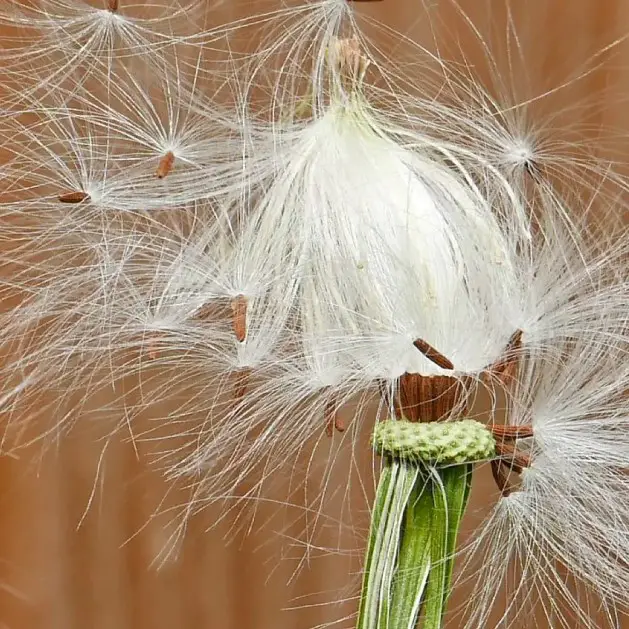
Achenes and cypselas are two distinct types of dry, one-seeded fruits. While they have some similarities, there are also some key differences between the two.
In this blog post, we’ll take a look at what achenes and cypselas are, how they are similar, and how they differ from each other. We’ll also explore some of the common examples of each type of fruit.
Characteristics of achene

An achene is a type of small, dry fruit that is found in many flowering plants. It has a single seed, is hard, and usually does not have any distinct features like a shape or color. It is often mistaken for a cypsela, which is also a small, dry fruit.
However, there are some key differences between achenes and cypselas. While an achene has a single seed, a cypsela usually has several seeds.
Achenes are also usually smaller than cypselas, and lack any distinct features that would make them stand out. The biggest difference between the two is that an achene has a thin, papery, or membranous covering, while a cypsela does not.
Characteristics of cypsela
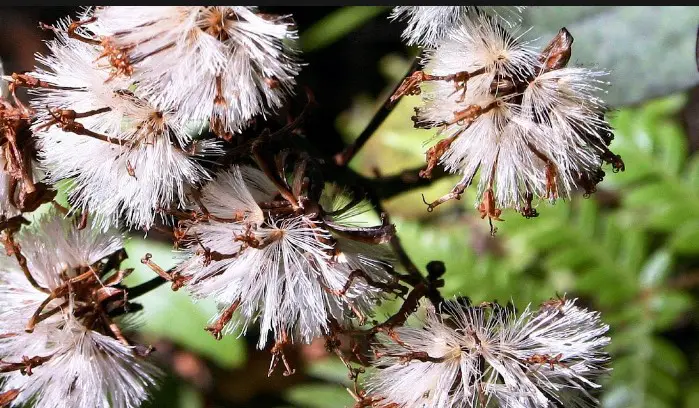

Cypsela is a type of dry, one-seeded fruit, similar to achene, which is also a dry, one-seeded fruit. The main difference between the two is that the pericarp of a cypsela is fused with the seed coat, while the pericarp of an achene is free from the seed coat.
Another difference is that the pericarp of a cypsela is usually thin and papery, while the pericarp of an achene is usually thick and leathery. In addition, the seed of a cypsela is usually small, while the seed of an achene is usually larger. Finally, a cypsela is often winged, while an achene is rarely winged.
Examples of achene and cypsela
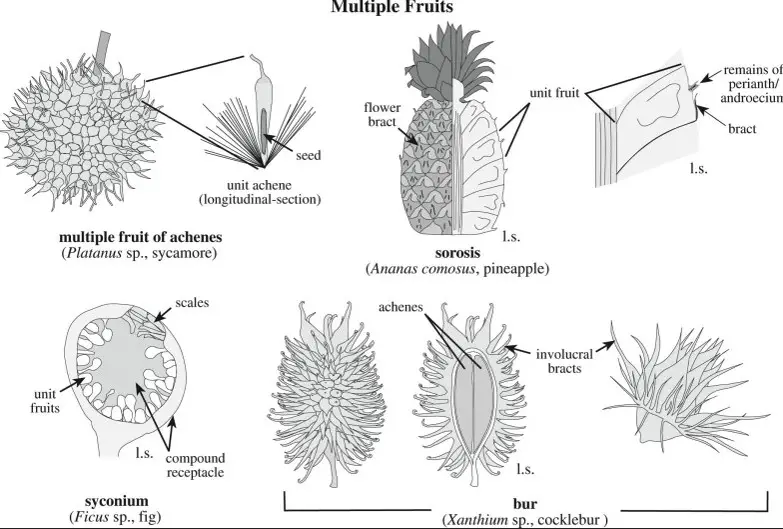
Achenes and cypselas are both small, dry fruits that are derived from a single carpel. While these two fruits may look similar, they are actually quite different. Achenes are typically thin-walled, one-seeded fruits that are formed from a simple ovary.
Achenes are typically thin-walled, one-seeded fruits that are formed from a simple ovary. Cypselas, on the other hand, are generally small and indehiscent, meaning that they do not open to release the seeds. Cypselas are also usually slightly thicker-walled than achenes and often contain several small seeds.
An example of an achene is a sunflower seed, while an example of a cypsela is a dandelion seed. Ultimately, the main difference between achenes and cypselas is the way in which they are formed and the amount of seeds they contain.
Benefits of achene and cypsela
When it comes to differentiating between achenes and cypselas, the main distinction is in their shape. Achenes are small, dry, indehiscent fruits, usually with a single seed, while cypselas are small, dry, indehiscent fruits with multiple seeds. Achenes often have a thin and papery outer coating, while cypselas are usually smooth and thin.
Achenes often have a thin and papery outer coating, while cypselas are usually smooth and thin. Given their different shapes, achenes and cypselas each have their own set of benefits. Achenes are extremely lightweight and can be easily dispersed by wind, which helps with the spread of the plant.
Cypselas, on the other hand, are heavier and are usually dispersed by animals, which helps with the spread of the plant in a different way. Additionally, since achenes and cypselas are both dry and indehiscent, they can survive for long periods of time in various conditions, making them ideal for long-term storage.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the major difference between an achene and a cypsela is the type of fruits they produce. Achenes produce a single-seeded fruit with a hard outer coat, while cypselas produce a single-seeded fruit with a thin, papery outer layer.
Both types of fruits are important for dispersing seeds and maintaining plant populations.

