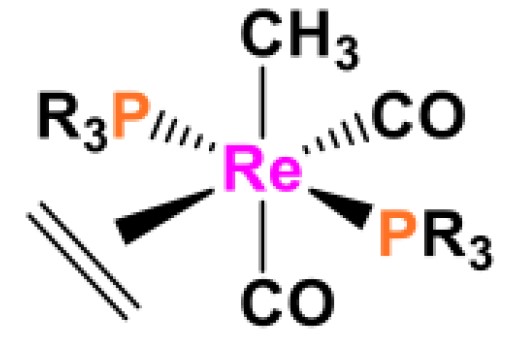
The 18 electron rule and EAN rule are two important concepts in chemistry. By understanding the difference between the two, chemists can better determine the stability and reactivity of molecules. In this blog, we’ll explore the subtle yet important differences between the 18 electron rule and EAN rule, and examine the implications of each.
Overview of the differences between 18 electron rule and ean rule
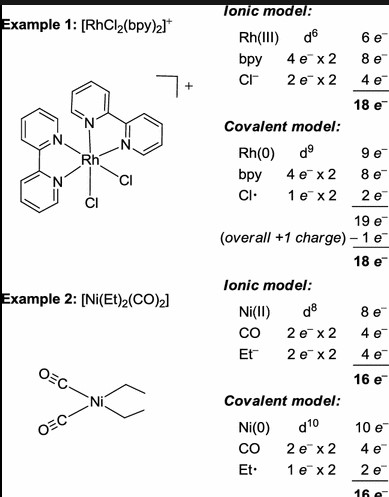
The 18 electron rule and ean rule are two important concepts in organic chemistry, and it is important to understand the differences between them. The 18 electron rule states that a transition metal complex should contain 18 valence electrons, while the ean rule states that a transition metal complex should contain a set number of electrons associated with each ligand. This means that there can be variations in the number of electrons depending on the number of ligands, but the total number of electrons must be equal to 1
Thus, the 18 electron rule is a set number of electrons for a single transition metal complex, while the ean rule is a set number of electrons associated with each ligand in a transition metal complex.
Exploring the origin of 18 electron rule and ean rule
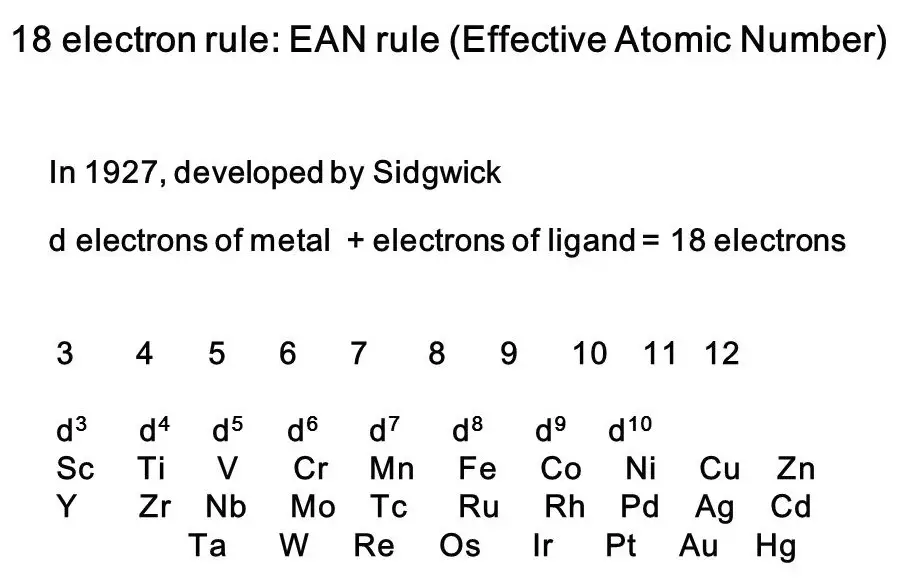
The 18 electron rule and the ean rule are two important concepts in chemistry that have been used to explain the stability of certain molecules. Despite their similarities, there are some key differences between the two rules.
The 18 electron rule states that closed-shell molecules composed of transition metals and their ligands should have 18 valence electrons in their molecular orbitals. On the other hand, the ean rule states that molecules should have a total of 8 electrons in their valence orbitals. This means that the 8 electrons should be shared between the metal and the ligands.
While both of these rules help explain the stability of molecules, the 18 electron rule is more applicable to transition metals, while the ean rule is more applicable to main group elements. Additionally, the 18 electron rule does not take into account the degree of covalency of the bond between the metal and the ligand, while the ean rule considers this factor. Ultimately, the 18 electron rule and the ean rule are both important rules for understanding the stability of molecules, but they are not interchangeable.
Comparing the application of 18 electron rule and ean rule
The 18 electron rule and EAN rule are both useful tools to predict the stability of a molecule. The 18 electron rule seeks to explain the relative stability of a molecule by counting the total number of electrons in the valence shell of the central atom.
If the total number of electrons is equal to 18, then the molecule is considered stable. On the other hand, the EAN rule is used to determine the relative stability of a molecule by counting the number of electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. If the number of electron pairs is equal to 8, then the molecule is considered to be stable.
While both of these rules focus on the same concept, they differ in their approach. The 18 electron rule is simpler since it only requires counting the total number of electrons in the valence shell, while the EAN rule is more complex as it requires counting the number of electron pairs in the valence shell.
Analyzing the benefits and drawbacks of 18 electron rule and ean rule
The 18 electron rule and the EAN rule are two important concepts in chemistry for understanding the structure and reactivity of molecules. While the 18 electron rule is used to predict the stability of a given molecule, the EAN rule is used to predict the reactivity of a molecule.
The 18 electron rule states that the most stable configurations for molecules are those with 18 electrons in the valence shell, while the EAN rule states that molecules with 16 or 18 electrons in the valence shell are more reactive than those with 14 or fewer electrons. While both rules are useful for predicting the behavior of molecules, it is important to note that the 18 electron rule is more accurate in predicting stability, while the EAN rule is more accurate in predicting reactivity.
Exploring how 18 electron rule and ean rule are used in practice
The 18 electron rule and the EAN rule are two important concepts in the field of chemistry. While both these rules are used to predict the stability of a certain molecular structure, there is a key difference between them.
On the other hand, the EAN rule states that the most stable structure of a molecule is when it has a double bond between two elements with a larger difference in electronegativity. Thus, while the 18 electron rule focuses on the number of electrons present in a molecule, the EAN rule focuses on the bonding interactions between the elements.
In practice, both rules can be used to predict the most stable structure of a molecule, but the EAN rule provides more accurate results.
Conclusion
The 18 electron rule and the EAN rule are two different ways of understanding the same concept. The 18 electron rule states that electrons in the outer shell of a transition metal should be arranged in sets of eight, while the EAN rule states that electrons in the outer shell should be arranged in sets of two, four, and six.
Ultimately, both rules can be used to predict the likely stability of a given metal complex, but the EAN rule is more accurate in predicting the most stable configuration.