Insulin and potassium are two vital components in the human body, each playing critical roles in our overall health. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, is primarily associated with the regulation of glucose levels in the blood. Potassium, on the other hand, is a crucial mineral that is necessary for the proper functioning of nerve signals, muscle contractions, and fluid balance in the body. The relationship between these two is complex and has significant implications for metabolic health and disease management.
The interplay between insulin and potassium revolves around their essential roles in cellular functions. Insulin helps to lower blood glucose levels and facilitates the entry of potassium into cells, maintaining the body’s electrolyte balance. This process is critical for preventing conditions such as hypokalemia (low potassium levels) or hyperkalemia (high potassium levels), which can have serious health implications.
Understanding the dynamics between insulin and potassium is crucial, especially for individuals with conditions like diabetes, where insulin management is a daily concern. The balance between these two elements affects numerous bodily functions, including heart rhythm, muscle function, and the nervous system’s operations. This intricate relationship underscores the importance of maintaining healthy levels of both insulin and potassium for optimal health.
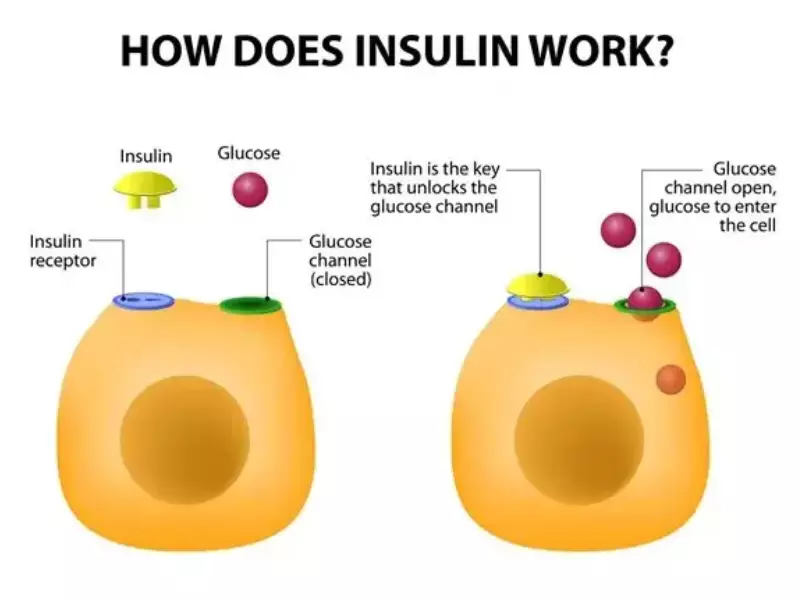
Insulin Overview
Definition and Function
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, specifically in the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans. Its primary role is to regulate blood glucose levels. When you eat, carbohydrates in your food are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. High blood glucose levels stimulate the pancreas to release insulin, which allows cells in the body to absorb glucose and use it for energy. Insulin also helps store glucose in the liver and muscles as glycogen for use when the body needs more energy.
Insulin’s Role in Glucose Metabolism
The process of glucose metabolism is critical for maintaining energy balance in the body. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, thus lowering blood glucose levels. It acts like a key, unlocking cells to allow glucose to enter. Without insulin, glucose cannot be utilized by most body cells. This is why individuals with diabetes, who have impaired insulin production or function, experience high blood glucose levels.
Potassium Basics
What is Potassium?
Potassium is an essential mineral and electrolyte necessary for various bodily functions. It’s involved in muscle contractions, nerve signal transmission, and maintaining fluid balance within the body. Most potassium in the body is found inside cells, with a small amount present in the blood.
Key Functions in the Body
Potassium is vital for:
- Muscle function: It enables muscle contraction, including the heartbeat.
- Nerve function: It helps transmit nerve signals.
- Fluid balance: It regulates the balance of fluids inside and outside cells.
Insulin and Potassium Connection
Biochemical Link
The relationship between insulin and potassium is rooted in their shared role in cellular function. Insulin not only helps glucose enter cells but also influences the movement of potassium into cells. This action is essential for maintaining electrolyte balance and proper cellular function.
How Insulin Affects Potassium Levels
When insulin binds to its receptors on cell surfaces, it stimulates potassium uptake by cells. This reduces potassium levels in the blood, highlighting insulin’s role in potassium regulation. For individuals with insulin resistance or diabetes, this process can be impaired, leading to challenges in maintaining normal potassium levels.
Potassium Regulation
Normal Potassium Levels
The normal range for potassium in the blood is typically between 3.5 and 5.0 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Keeping potassium within this range is crucial for preventing health issues.
Factors Influencing Potassium Balance
Several factors can affect potassium levels, including:
- Diet: Consumption of potassium-rich foods.
- Water intake and loss: Through urine and sweat.
- Medications: Certain drugs can affect potassium levels.
- Health conditions: Such as kidney disease, which affects potassium excretion.
Insulin’s Role in Potassium Management
Mechanisms of Action
Insulin helps maintain potassium balance by:
- Promoting potassium entry into cells: This action lowers potassium levels in the blood.
- Influencing renal potassium handling: Insulin affects how the kidneys process and excrete potassium.
Clinical Implications
Understanding insulin’s role in potassium management is essential for treating conditions like hyperkalemia (high potassium levels) in patients with diabetes or those with acute rises in potassium due to other medical conditions.
Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia
Definitions and Causes
- Hypokalemia refers to low potassium levels in the blood, which can be caused by inadequate potassium intake, increased loss of potassium (through urine or gastrointestinal tract), or shifts of potassium into cells.
- Hyperkalemia is the condition of having too much potassium in the blood, often resulting from kidney dysfunction, tissue breakdown, or medications affecting potassium balance.
Symptoms and Risks
- Hypokalemia symptoms include muscle weakness, cramps, and irregular heartbeats.
- Hyperkalemia can lead to muscle weakness, paralysis, and life-threatening heart rhythm problems.
Insulin Therapy in Potassium Management
Treating High Potassium
Treating high potassium (hyperkalemia) often involves insulin therapy to help move potassium from the blood into cells. This treatment can be critical in acute cases, where high potassium levels threaten heart function. Insulin, given alongside glucose to prevent hypoglycemia, facilitates the cellular uptake of potassium, effectively lowering its blood levels.
Considerations and Protocols
When using insulin to manage potassium levels, healthcare providers follow specific protocols. These include:
- Monitoring blood glucose levels closely to avoid hypoglycemia.
- Administering glucose with insulin to maintain blood sugar levels.
- Adjusting doses based on the patient’s insulin sensitivity and potassium levels.
Health Implications
Diabetes and Potassium Imbalance
Individuals with diabetes face challenges in maintaining potassium balance due to fluctuations in insulin levels. Both hyperkalemia and hypokalemia can occur, complicating diabetes management. Monitoring and managing blood glucose and potassium levels are essential for preventing these imbalances.
Cardiovascular Health
The relationship between potassium levels, insulin sensitivity, and cardiovascular health is significant. Imbalances in potassium can lead to heart rhythm problems, while insulin resistance is associated with increased cardiovascular risk. Maintaining optimal levels of both can support heart health.
Diet and Lifestyle
Potassium-Rich Foods
Incorporating potassium-rich foods into your diet is a natural way to help manage potassium levels. Examples include:
- Bananas
- Sweet potatoes
- Spinach
- Avocadoes
- Beans
Eating a variety of these foods can help maintain normal potassium levels and support overall health.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Insulin and Potassium
Several lifestyle factors can influence insulin and potassium balance, including:
- Physical activity: Enhances insulin sensitivity and affects potassium distribution in the body.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake helps regulate potassium levels.
- Diet: A balanced intake of nutrients supports both insulin and potassium balance.
Research and Studies
Recent Findings
Recent research has shed light on the intricate connections between insulin resistance, potassium balance, and health outcomes. Studies indicate that improving insulin sensitivity may help regulate potassium levels, potentially reducing the risk of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia.
Ongoing Research Directions
Ongoing research aims to further understand the mechanisms behind insulin’s role in potassium management. This includes studying the effects of different diets, medications, and lifestyle modifications on this balance and their implications for health.
Practical Tips
Monitoring Potassium Levels
Regular monitoring of potassium levels is important, especially for individuals at risk of imbalances, such as those with kidney disease or diabetes. This can involve blood tests and working closely with healthcare providers to adjust diet and medications as needed.
Managing Insulin Sensitivity
Improving insulin sensitivity can have positive effects on both glucose and potassium regulation. Tips for managing insulin sensitivity include:
- Regular physical activity: Exercise helps improve the body’s use of insulin.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess body fat, especially around the waist, can decrease insulin sensitivity.
- Eating a balanced diet: Emphasizing whole foods over processed ones can help manage blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
FAQs
How Does Insulin Affect Potassium Levels?
Insulin helps to regulate potassium levels in the blood by stimulating the movement of potassium from the bloodstream into the cells. This process is vital for maintaining normal potassium levels and preventing hyperkalemia, especially in individuals with conditions affecting insulin production or action, such as type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
What Happens When Potassium Levels Are Too High or Too Low?
High potassium levels, or hyperkalemia, can lead to dangerous heart irregularities and muscle weakness. Low potassium levels, or hypokalemia, can cause muscle cramps, weakness, fatigue, and even affect heart function. Balancing potassium levels is crucial for maintaining healthy muscle and nerve function.
Can Diet Influence Insulin and Potassium Balance?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in managing both insulin and potassium balance. Foods rich in potassium, such as bananas, oranges, potatoes, and spinach, can help maintain normal potassium levels. Meanwhile, a balanced diet that moderates sugar and carbohydrate intake can support healthy insulin levels and sensitivity.
How Do Health Conditions Like Diabetes Affect Potassium Levels?
Diabetes, especially when poorly controlled, can significantly impact potassium levels. High blood sugar levels can lead to increased urinary potassium loss, while insulin therapy might cause potassium to move into cells, potentially leading to hypokalemia or hyperkalemia under different circumstances.
Conclusion
The relationship between insulin and potassium is a fine balance, crucial for maintaining many of the body’s vital functions. Disruptions in this balance can lead to significant health issues, highlighting the importance of understanding and managing these elements. For individuals, particularly those with conditions like diabetes, awareness and active management of insulin and potassium levels are essential for sustaining health and preventing complications.
The interdependency of insulin and potassium underscores the complexity of the body’s metabolic processes and the importance of a holistic approach to health. By recognizing the signs of imbalance and adopting lifestyle and dietary habits that support the optimal functioning of these elements, individuals can contribute significantly to their overall well-being and longevity.
